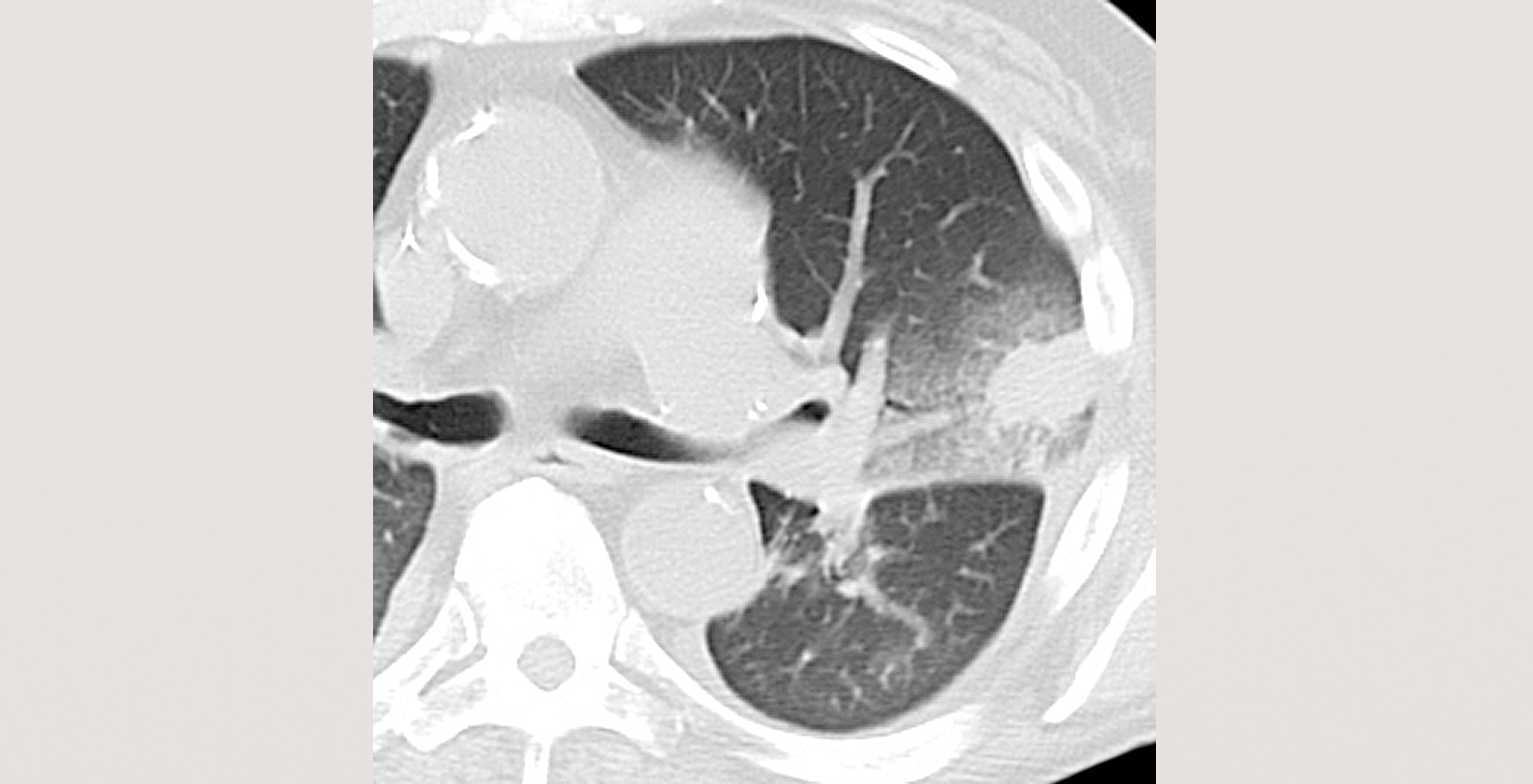
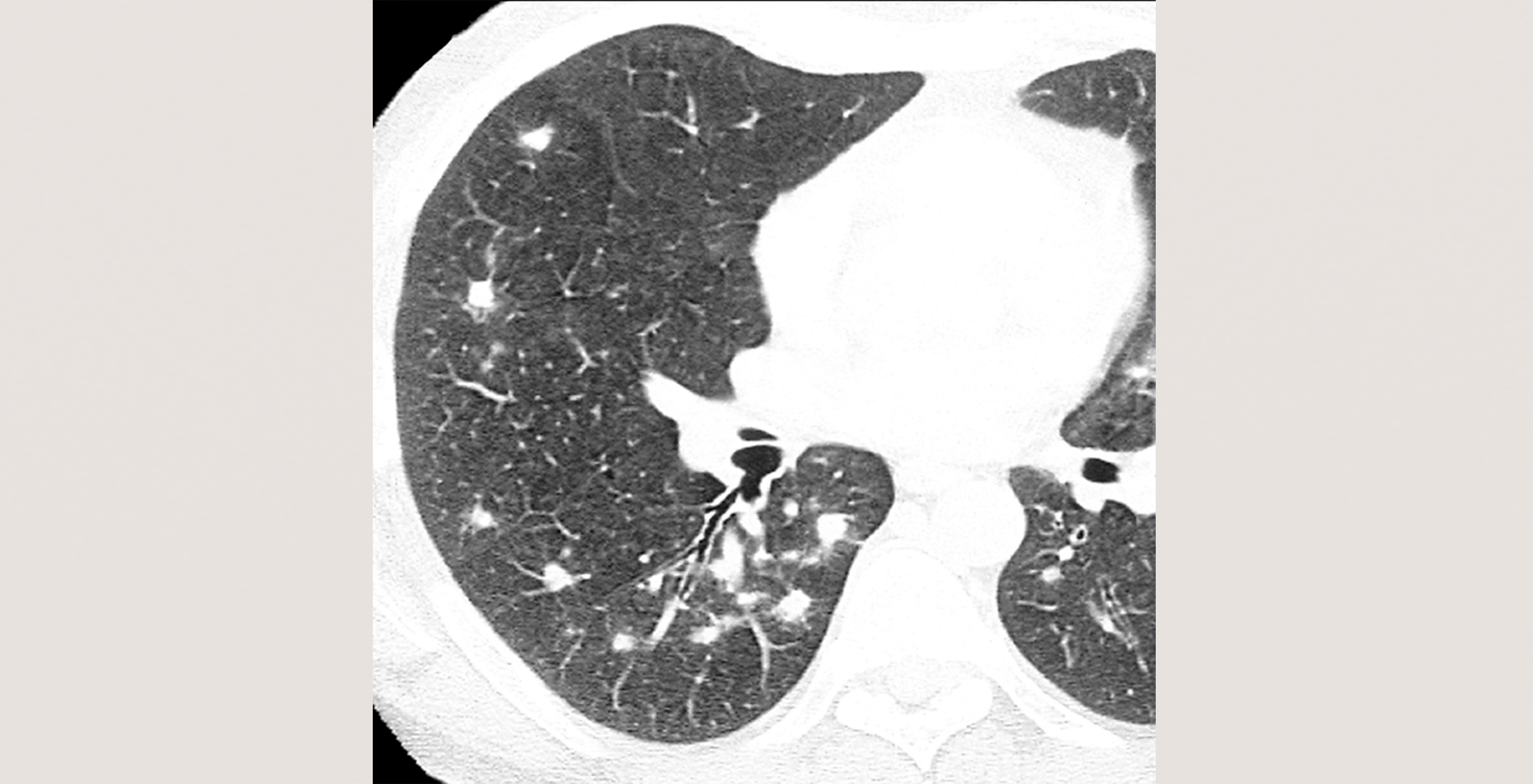
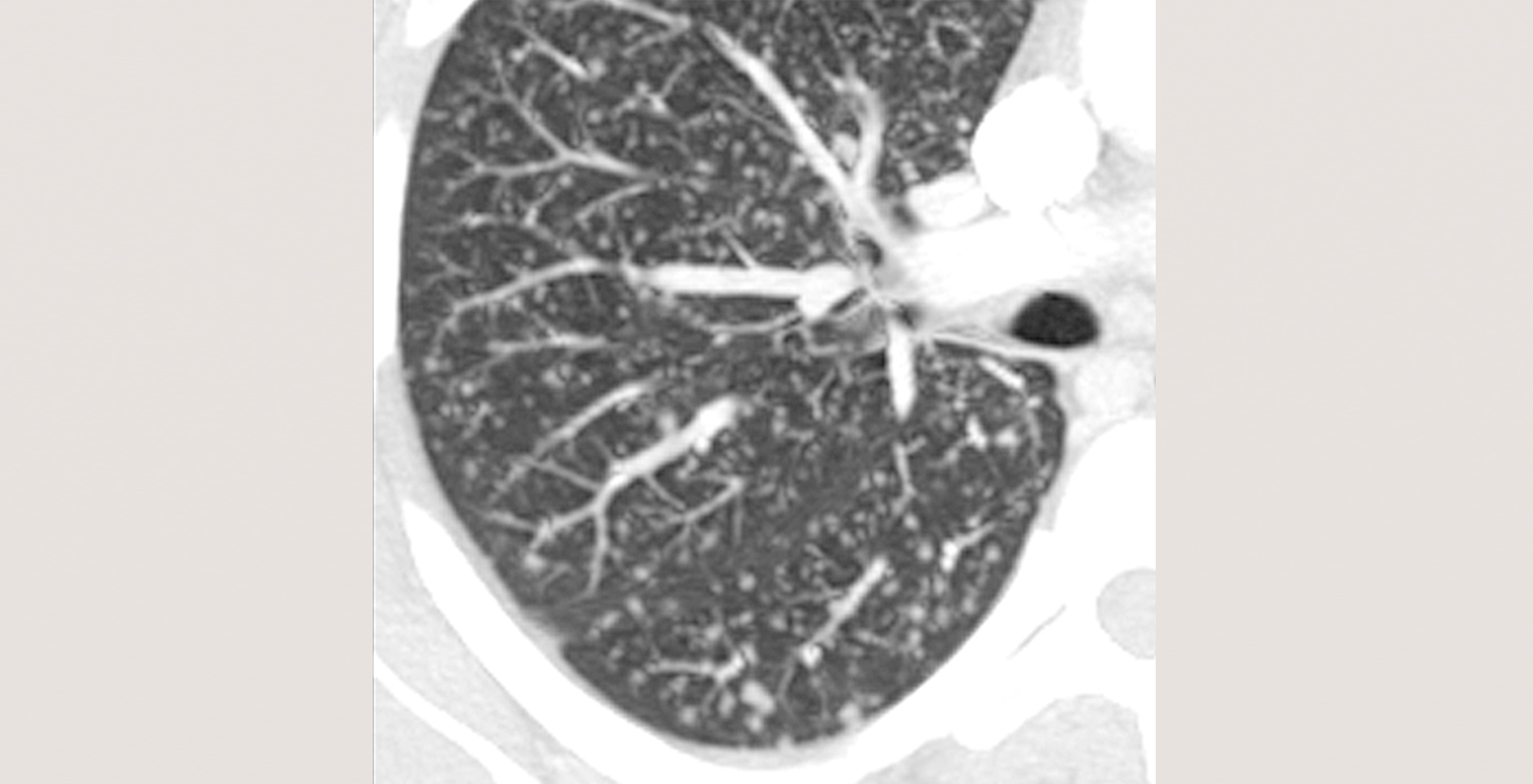
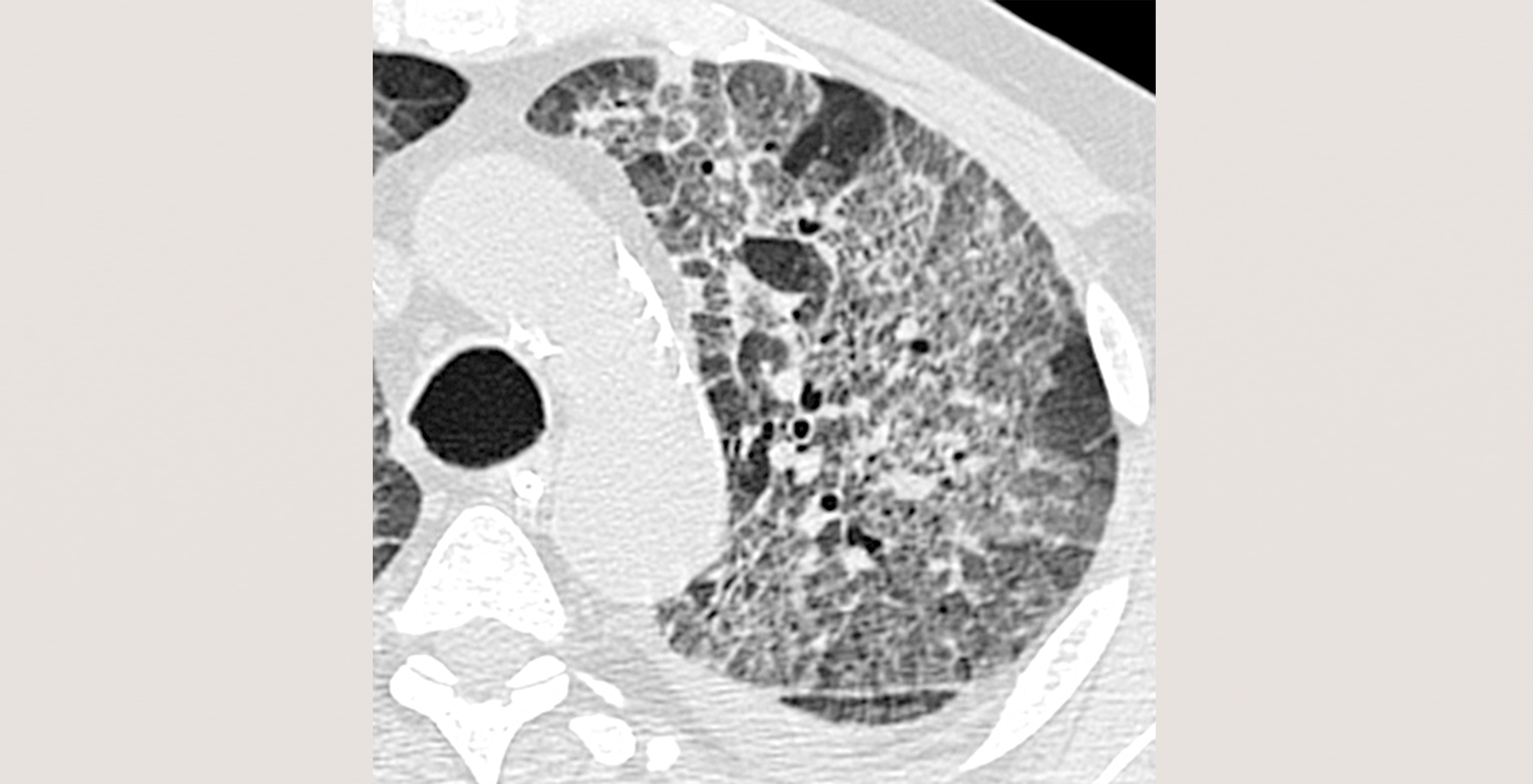
Review key facts, bulleted text, essential images and current references.
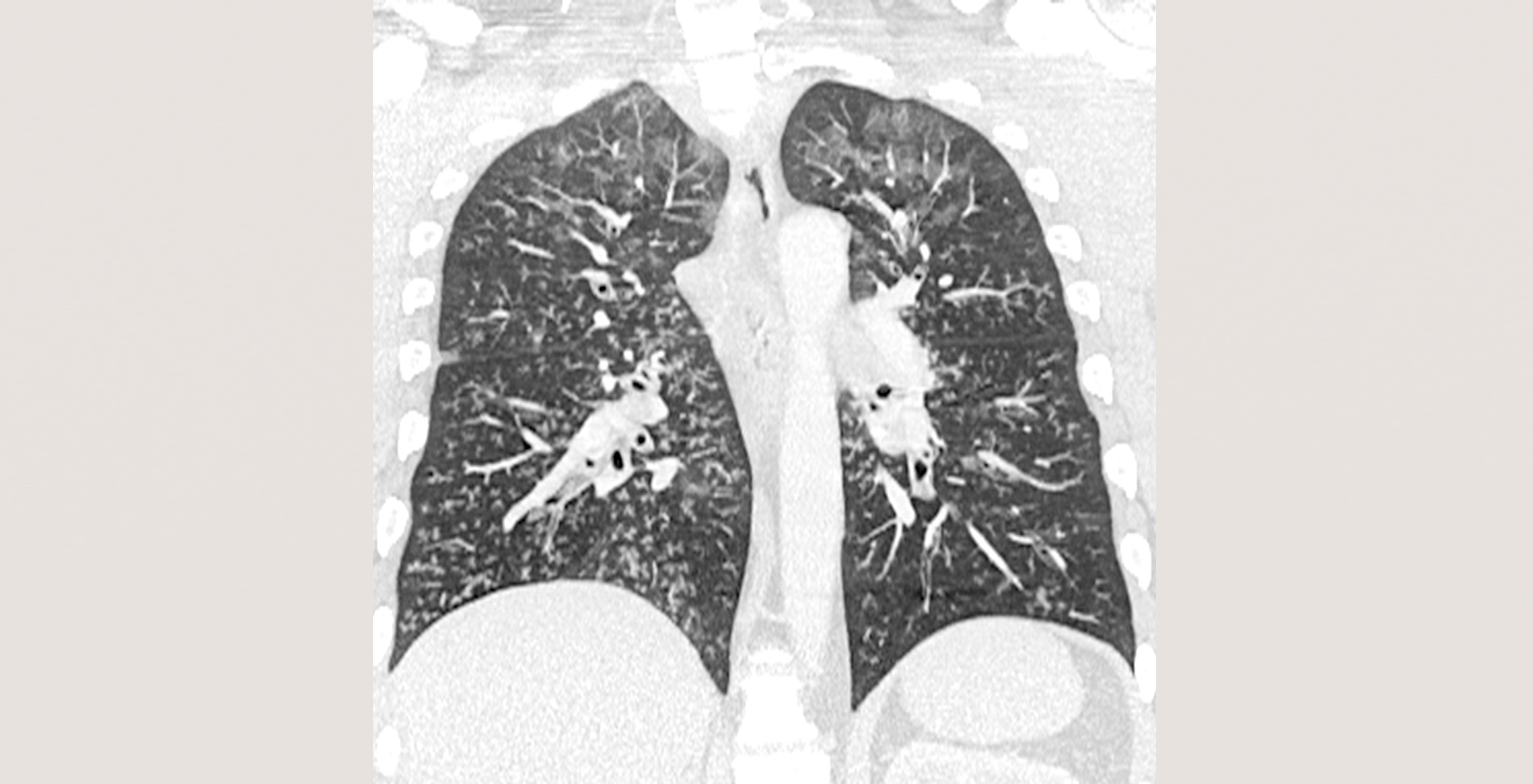

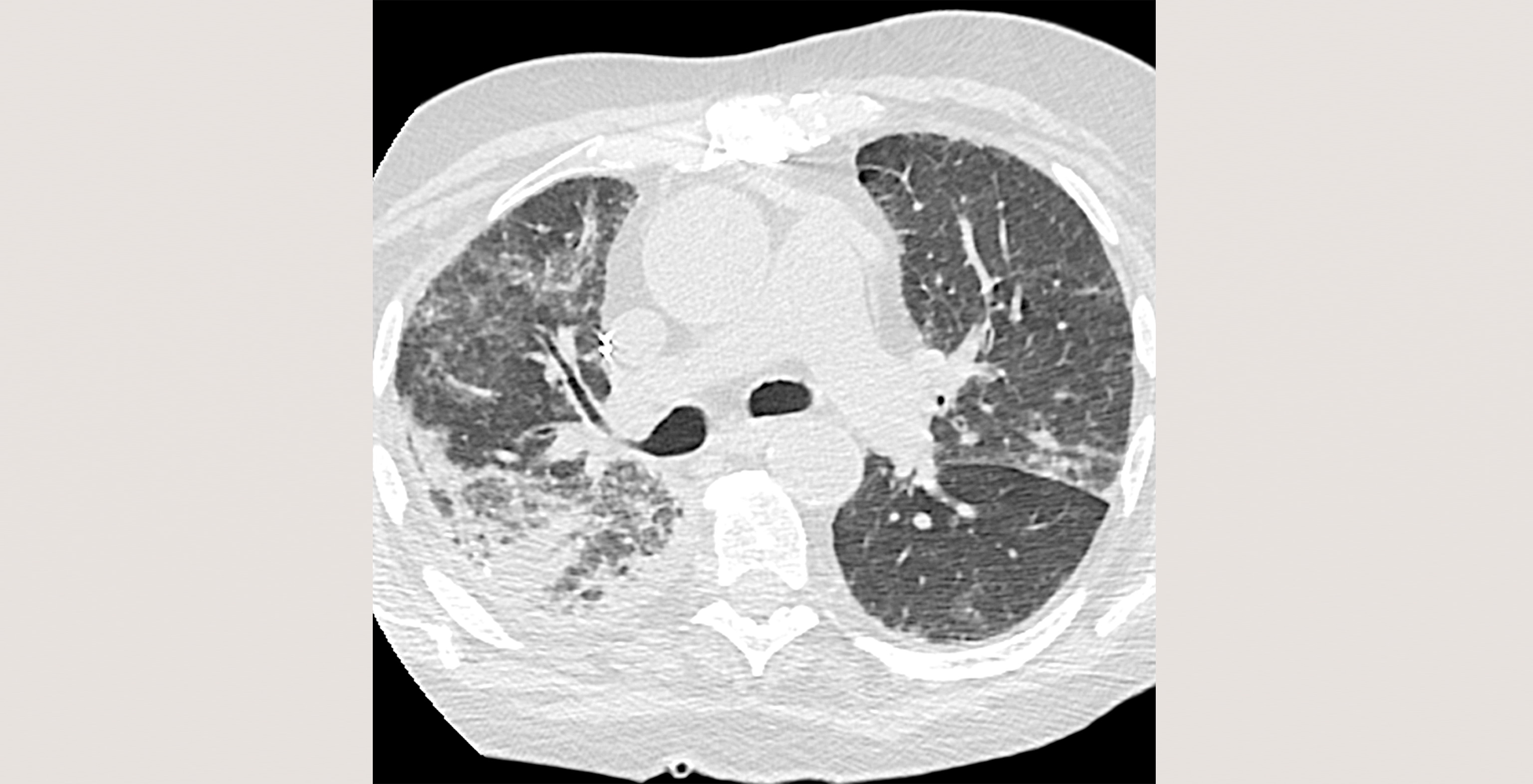
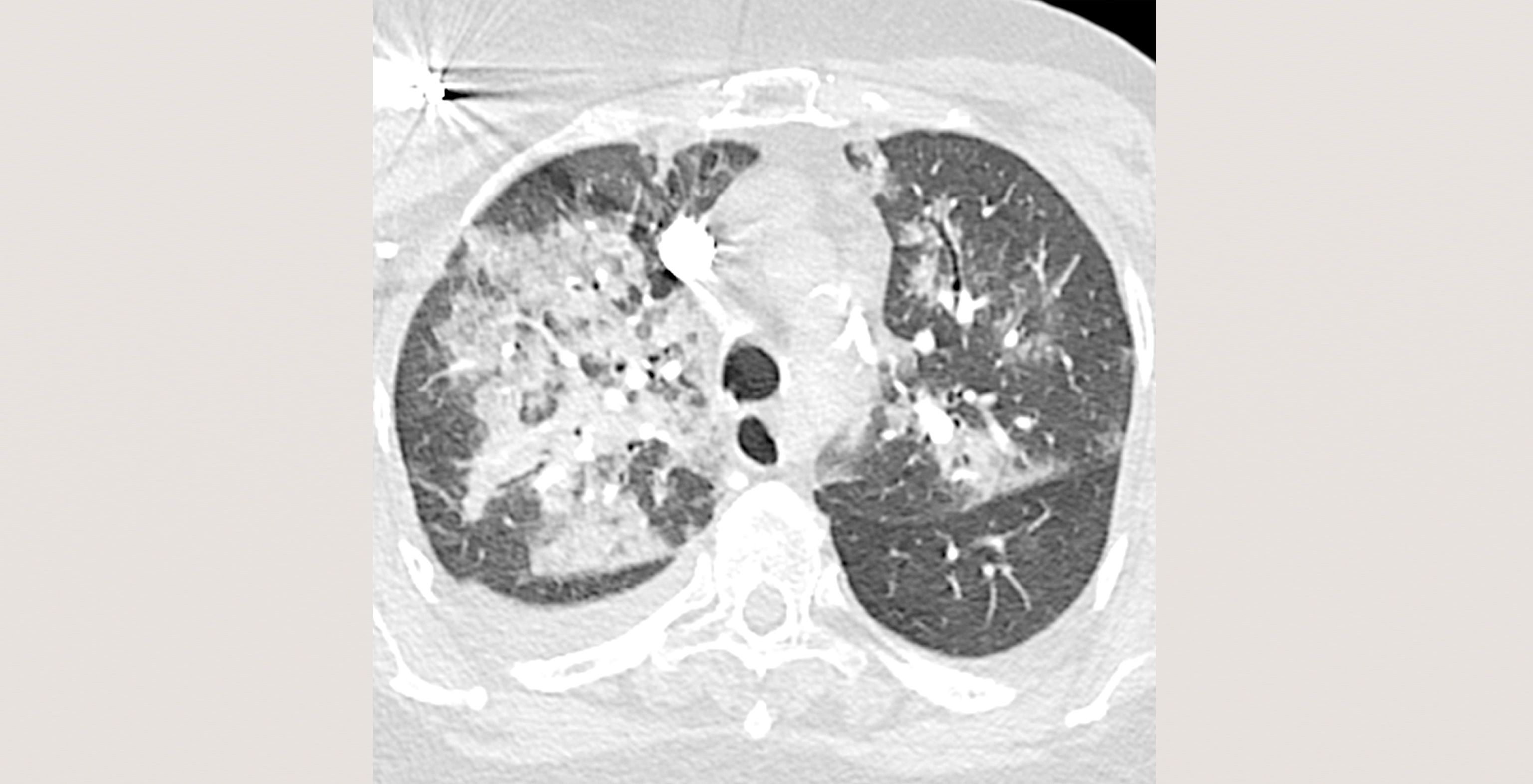
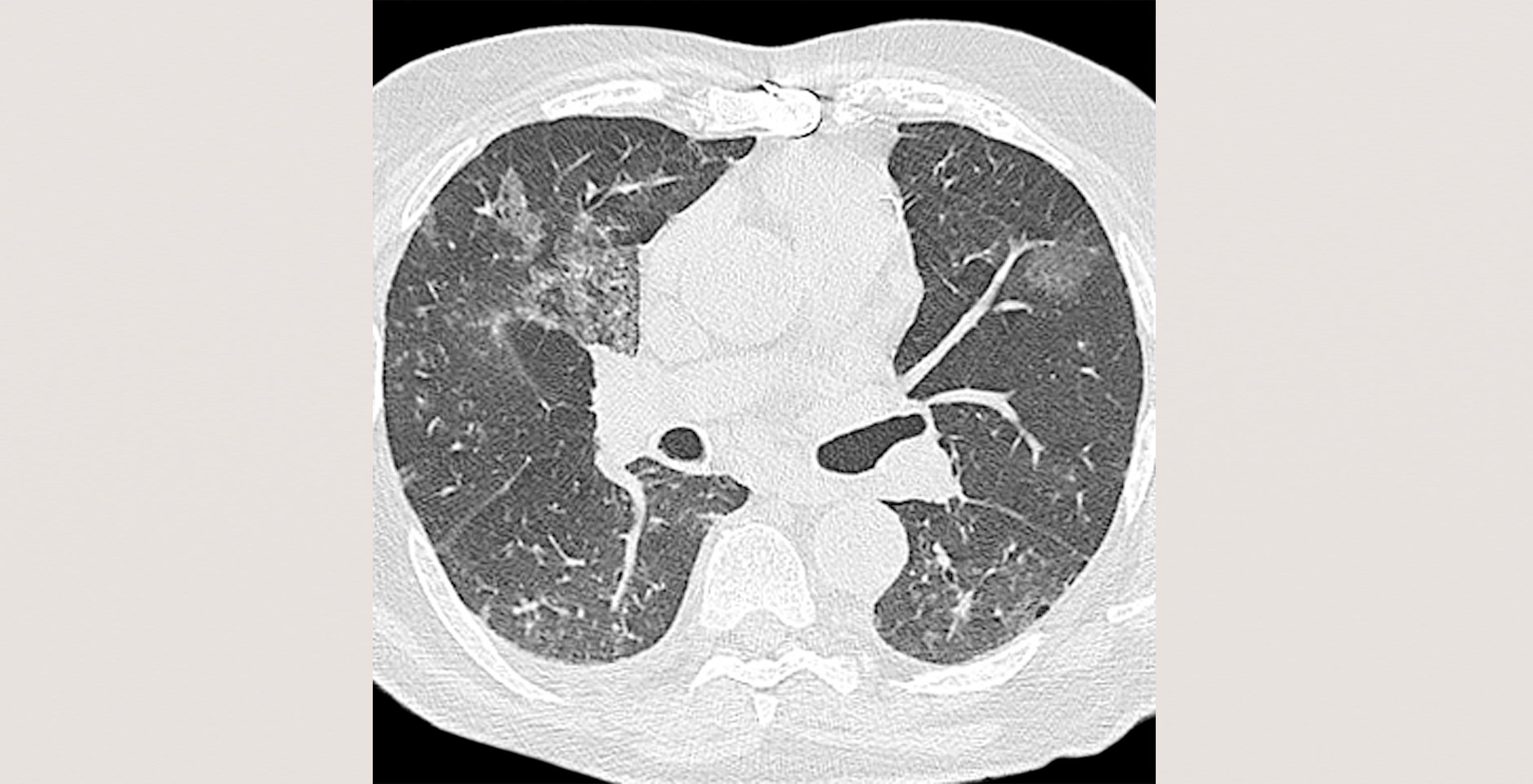

Cookies são usados neste site. Para recusar ou saber mais, visite nosso página de cookies.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier, its licensors, and contributors. All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.