ThisisPatientEngagementcontent
Chlamydia, Female
To download the Ukraine translated version, please click the link below
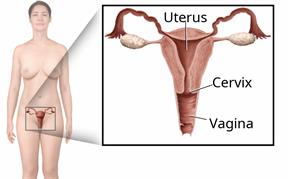
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). This kind of infection spreads through sexual contact.
Chlamydia can occur in different places in the body, including:Chlamydia isn't hard to treat. But if it is not treated, it can cause worse health problems, such as pelvic inflammatory disease, also called PID. PID can increase your risk of not being able to have children.
Also, if you are pregnant or get pregnant and have untreated chlamydia:This condition is caused by a germ (bacteria) called Chlamydia trachomatis. This germ is spread from an infected partner during sex.
The infection can spread through contact with:In some cases, there are no symptoms, especially early in the infection.
If you get symptoms, they may include:This infection is treated with antibiotics.
Sexual activity
General instructions
 To lower your risk:
To lower your risk:This information is not intended to replace advice given to you by your health care provider. Make sure you discuss any questions you have with your health care provider.
Cookies are used by this site. To decline or learn more, visit our cookie notice.
Copyright © 2025 Elsevier, its licensors, and contributors. All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.