ThisisPatientEngagementcontent
Contraception Choices
To download the Ukraine translated version, please click the link below
Birth control is also called contraception. Birth control prevents pregnancy.
There are many types of birth control. Work with your health care provider to find the best option for you.
These types of birth control have hormones in them to prevent pregnancy.
Birth control implant
This is a small tube that is put into the skin of your arm. The tube can stay in for up to 3 years.
Birth control shot
These are shots you get every 3 months.
Birth control pills
This is a pill you take every day. You need to take it at the same time each day.
Birth control patch
This is a patch that you put on your skin. You change it 1 time each week for 3 weeks. After that, you take the patch off for 1 week.
Vaginal ring

This is a soft plastic ring that you put in your vagina. The ring is left in for 3 weeks. Then, you take it out for 1 week. Then, you put a new ring in.
Male condom
This is a thin covering that you put on the penis before sex. The condom is thrown away after sex.
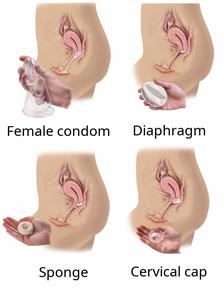
Female condom
This is a soft, loose covering that you put in the vagina before sex. The condom is thrown away after sex.
Diaphragm
A diaphragm is a soft barrier that is shaped like a bowl. It must be made to fit your body. You put it in the vagina before sex with a chemical that kills sperm called spermicide. A diaphragm should be left in the vagina for 6–8 hours after sex and taken out within 24 hours.
You need to replace a diaphragm:Cervical cap
This is a small, soft cup that fits over the cervix. The cervix is the lowest part of the uterus. It's put in the vagina before sex, along with spermicide. The cap must be made for you. The cap should be left in for 6–8 hours after sex. It is taken out within 48 hours.
A cervical cap must be prescribed and fit to your body by a provider. It should be replaced every 2 years.
Sponge
This is a small sponge that is put into the vagina before sex. It must be left in for at least 6 hours after sex. It must be taken out within 30 hours and thrown away.
Spermicides
These are chemicals that kill or stop sperm from getting into the uterus. They may be a pill, cream, jelly, or foam that you put into your vagina. They should be used at least 10–15 minutes before sex.
Female tubal ligation
This is surgery to block the fallopian tubes.
Male sterilization
This is a surgery, called a vasectomy, to tie off the tubes that carry sperm in men. This method takes 3 months to work. Other forms of birth control must be used for 3 months.
This information is not intended to replace advice given to you by your health care provider. Make sure you discuss any questions you have with your health care provider.
Cookies are used by this site. To decline or learn more, visit our cookie notice.
Copyright © 2025 Elsevier, its licensors, and contributors. All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.