Diabetes Mellitus and Foot Care
Diabetes, also called diabetes mellitus
, may cause problems with your feet and legs because of poor blood flow (
circulation). Poor circulation may make your skin:
You may also have nerve damage (neuropathy). This can cause decreased feeling in your legs and feet. This means that you may not notice minor injuries to your feet that could lead to more serious problems. Finding and treating problems early is the best way to prevent future foot problems.
How to care for your feet
Foot hygiene
-
Wash your feet daily with warm water and mild soap. Do not use hot water. Then, pat your feet and the areas between your toes until they are fully dry. Do not soak your feet. This can dry your skin.
-
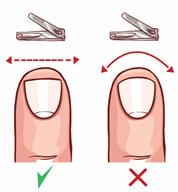
Trim your toenails straight across. Do not dig under them or around the cuticle. File the edges of your nails with an emery board or nail file.
-
Apply a moisturizing lotion or petroleum jelly to the skin on your feet and to dry, brittle toenails. Use lotion that does not contain alcohol and is unscented. Do not apply lotion between your toes.
Shoes and socks
-
Wear clean socks or stockings every day. Make sure they are not too tight. Do not wear knee-high stockings. These may decrease blood flow to your legs.
-
Wear shoes that fit well and have enough cushioning. Always look in your shoes before you put them on to be sure there are no objects inside.
-
To break in new shoes, wear them for just a few hours a day. This prevents injuries on your feet.
Wounds, scrapes, corns, and calluses
-
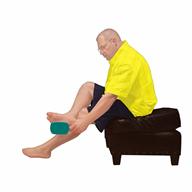
Check your feet daily for blisters, cuts, bruises, sores, and redness. If you cannot see the bottom of your feet, use a mirror or ask someone for help.
-
Do not cut off corns or calluses or try to remove them with medicine.
-
If you find a minor scrape, cut, or break in the skin on your feet, keep it and the skin around it clean and dry. You may clean these areas with mild soap and water. Do not clean the area with peroxide, alcohol, or iodine.
- If you have a wound, scrape, corn, or callus on your foot, look at it several times a day to make sure it is healing and not infected. Check for:
General tips
-
Do not cross your legs. This may decrease blood flow to your feet.
-
Do not use heating pads or hot water bottles on your feet. They may burn your skin. If you have lost feeling in your feet or legs, you may not know this is happening until it is too late.
-
Protect your feet from hot and cold by wearing shoes, such as at the beach or on hot pavement.
-
Schedule a complete foot exam at least once a year or more often if you have foot problems. Report any cuts, sores, or bruises to your health care provider right away.
Contact a health care provider if:
-
You have a condition that increases your risk of infection, and you have any cuts, sores, or bruises on your feet.
-
You have an injury that is not healing.
-
You have redness on your legs or feet.
-
You feel burning or tingling in your legs or feet.
-
You have pain or cramps in your legs and feet.
-
Your legs or feet are numb.
-
Your feet always feel cold.
-
You have pain around any toenails.
- You have a wound, scrape, corn, or callus on your foot and:
This information is not intended to replace advice given to you by your health care provider. Make sure you discuss any questions you have with your health care provider.

