Uterine Tissue Growing Outside the Uterus (Endometriosis): What to Know
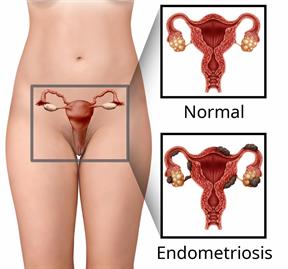
Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that forms the lining of the uterus grows in places outside the uterus. This tissue can grow in:
This tissue most often grows on the ovaries and on the lining of the pelvic cavity.
What are the causes?
The cause of this condition is not known.
What increases the risk?
-
Having a family history of endometriosis.
-
Having never given birth.
-
Starting your period at age 10 or younger.
What are the signs or symptoms?
Often, there are no symptoms of this condition. If you do have symptoms, they may include:
Heavy bleeding during your period.
Periods that happen more than once a month.
Not being able to get pregnant.
- Pain. You may feel pain:
Depending on where the changed tissue is growing, symptoms may:
Happen during your period (most often) or at the middle of your cycle.
Come and go. You may have no symptoms during some months.
Stop when you no longer have your periods (menopause).
How is this diagnosed?
This condition is diagnosed based on your symptoms and a physical exam. You may also have tests, such as:
Blood and pee tests to help rule out other causes.
Ultrasound to look for tissues that are not normal.
X-ray of the lower bowel.
CT scan.
MRI.
To confirm the diagnosis, your health care provider may:
How is this treated?
There's no cure for this condition. The treatment aims to control your symptoms. The type of treatment depends on whether you want to become pregnant in the future.
This condition may be treated with:
Pain medicines. These include NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen.
Hormones, such as birth control pills, to slow the growth of changed tissue.
- Surgery to remove the changed tissue.
Tissue may be removed using a laparoscope and a laser.
The ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus may be removed (hysterectomy). This is done in very severe cases.
Follow these instructions at home:
Take your medicines only as told.
-
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists:
acog.org
-
Contact a health care provider if:
-
You have irregular periods.
-
You have problems getting pregnant.
-
You have pain in your belly on the lower right side.
-
You have very bad pain that does not get better with medicine.
-
You have a high fever.
-
You have very bad throwing up or a feeling that you may throw up.
-
You have bloating and swelling in your belly.
-
You have pain when you poop, or you notice blood in your poop.
This information is not intended to replace advice given to you by your health care provider. Make sure you discuss any questions you have with your health care provider.
 Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that forms the lining of the uterus grows in places outside the uterus. This tissue can grow in:
Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that forms the lining of the uterus grows in places outside the uterus. This tissue can grow in: