Non-cancerous Breast Tumor (Fibroadenoma): What to Know
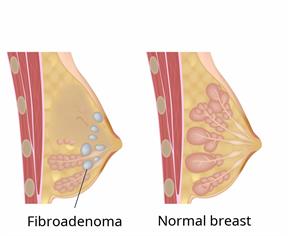
A fibroadenoma is a non-cancerous (benign) tumor in your breast. A tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue.
This kind of tumor is made up of breast tissue and the tissue that holds your breast together. The types are:
Simple. This is the most common type. It's when the tumor has only one type of tissue in it.
Complex. This is when there's more than one kind of tissue in the tumor. It could have pockets of fluid (cysts) and deposits of calcium in it.
Juvenile. This can form in female teens. It tends to grow bigger than other non-cancerous tumors.
If you have a complex or juvenile fibroadenoma, you may be more likely to get breast cancer in the future.
What are the causes?
The cause isn't known.
What are the signs or symptoms?
You may have no symptoms. Some tumors are too small to feel. If you can feel the tumor, it may feel like a lump in your breast that is:
You may have just one lump or more than one lump. You can get these lumps in one or both breasts.
How is this diagnosed?
A fibroadenoma may be diagnosed based on your symptoms, medical history, and an exam. You may also have tests. These may include:
An X-ray of your breast. This is called a mammogram.
An ultrasound. This can show if the lump is solid or filled with fluid. If there's fluid, some of it may be taken with a needle and tested.
A biopsy. This is when a small piece of tissue is removed from your breast for testing.
How is this treated?
Most fibroadenomas don't need to be treated. They often go away on their own. But treatment may include:
Follow these instructions at home:
-
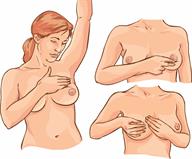
Do self-exams of your breast at home as told. Check the skin of your breasts and your nipples for any changes.
-
Do not smoke, vape, or use nicotine or tobacco.
-
Keep all follow-up visits. Your provider will check your breasts for any changes.
Contact a health care provider if:
- Your tumor:
Gets larger.
Feels different.
Starts to hurt.
- You have any other changes in your breast, such as:
This information is not intended to replace advice given to you by your health care provider. Make sure you discuss any questions you have with your health care provider.

