How to Use a Walker
This information provides guidance on how to use a walker. Your health care provider may give you more specific instructions based on your condition. They may also give you instructions on how to use your legs or arms to support your body weight.
What are the risks?
Using a walker is generally safe. But it may cause falls if it's not used correctly.
How to walk with a walker
The best way to use a walker depends on whether you're using a standard walker or a front-wheeled walker. For example:
A standard walker has rubber tips on the ends of all four legs.
A front-wheeled walker has wheels on the ends of the front legs and rubber tips on the ends of the back legs.
Do not use your walker on stairs or an escalator unless you've been trained by a physical therapist and your provider approves.
Standard walker

Pick up your walker. Do not slide your standard walker.
Set down your walker, one step-length in front of you. Make sure that all four legs of the walker touch the ground at the same time. Your toes should be farther forward than the back legs of your walker.
Hold on to the walker, and press it with your arms through handrails, as needed, for support.
Step your weaker leg into the middle of the walker. Step your stronger leg forward to land next to your weaker leg.
Repeat this process for each step.
Front-wheeled walker

Slide your front-wheeled walker one step-length in front of you. Your toes should be farther forward than the back legs of your walker.
Hold on to the walker for support and press through the handrails, as needed, for support.
Step your weaker leg into the middle of the walker. Step your stronger leg forward to land next to your weaker leg.
Repeat the process for each step.
Tips
Always keep both feet within the width of the walker's legs or wheels.
When using your walker, you should not feel like you need to lean forward or to the side to keep your hands on the handgrips.
Make sure you're following any weight-bearing instructions from your provider.
- If you have a standard walker:
- If you have a front-wheeled walker:
Be careful not to let the walker get too far ahead of you as you walk.
If your walker does not glide well over carpet, consider cutting an "X" into two tennis balls and placing the balls over the back legs of your walker.
How to stand up with a walker
-
Put your walker in front of you.
-
If your walker has brakes, place the brakes in the locked position.
-
Slide forward in your chair.
-
Position your legs so that your weaker leg is ahead of you and your stronger leg is bent and near your chair.
- Position your hands.
If your chair has armrests, put each hand on an armrest.
If there're no armrests, put the hand opposite your weaker leg on the chair seat, and put the other hand on the center of the walker's crossbar.
-
Lean forward and push up from your chair.
-
Rise by straightening your stronger leg.
-
Steady yourself.
-
Carefully move your hands to the handgrips of the walker.
Tips
How to sit down with a walker
Seat with armrests
-
Back up toward your seat, using your walker, until you feel the back of your legs touch the chair.
-
If your walker has brakes, place the brakes in the locked position.
-
Carefully reach your hands behind you and put each hand on an armrest.
-
Slowly lower yourself into the seat with your injured leg out in front.
Seat without armrests
-
Back up toward the side of the seat, using your walker, until you feel the back of your legs touch the chair.
-
If your walker has brakes, place the brakes in the locked position.
-
Use one hand to hold on to the back of the chair, and use the other hand to hold on to the front of the seat.
-
Slowly lower yourself into the seat with your injured leg out in front.
How to use a walker on a curb or step
Stepping up
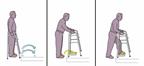
-
Put all four legs of the walker on the curb or step.
-
Get your feet as close to the curb or step as you can.
-
Test the steadiness of the walker by pressing down on the handgrips.
-
If the walker is steady, press down on it with your hands as you step up with your stronger leg.
-
Step up with your weaker leg.
Stepping down
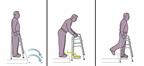
-
Put all four legs of the walker on the surface that's lower than the curb or step.
-
Get your feet as close to the curb or step as you can.
-
Test the steadiness of the walker by pressing down on the handgrips.
-
If the walker is steady, press down on it with your hands as you step down with your weaker leg.
-
Step down with your stronger leg.
This information is not intended to replace advice given to you by your health care provider. Make sure you discuss any questions you have with your health care provider.



