ThisiscontentfromElsevier'sDrugInformation
Ethinyl Estradiol; Norethindrone Acetate
Learn more about Elsevier's Drug Information today! Get the drug data and decision support you need, including TRUE Daily Updates™ including every day including weekends and holidays.
1 tablet (containing either 1 mg norethindrone acetate in combination with 20 mcg of ethinyl estradiol or alternatively, 1.5 mg norethindrone acetate in combination with 30 mcg of ethinyl estradiol) PO once daily for 21 days, followed by a period of 7 days without drug. Then, repeat cycle.[57612]
1 tablet (containing either 1 mg norethindrone acetate in combination with 20 mcg of ethinyl estradiol or alternatively, 1.5 mg norethindrone acetate in combination with 30 mcg of ethinyl estradiol) PO once daily for 21 days, followed by a period of 7 days without drug. Then, repeat cycle.[57612]
1 tablet (1 mg norethindrone acetate/0.02 mg ethinyl estradiol) PO once daily for 24 days, followed by 4 days of inert, inactive tablets. Repeat cycle every 28 days.[71231]
1 tablet (1 mg norethindrone acetate/0.02 mg ethinyl estradiol) PO once daily for 24 days, followed by 4 days of inert, inactive tablets. Repeat cycle every 28 days.[71231]
1 tablet PO once daily, in order directed on pack, following dosage as per routine contraception. Then, repeat cycles as directed for product chosen. Expected time to acne improvement with CHCs is usually within 3 to 6 months, and CHCs may be used with other acne therapies early in treatment to accelerate response. Prolonged treatment may be needed for acne control.[58791] [69506] [70323]
Follow dose as for routine contraception. Treatment for 6 to 12 months may be required; OCs have limited utility when the underlying cause of the condition is not related to a hypoestrogenic or hyperandrogenic state.[58791] [58792] [58793]
Follow dose as for routine contraception. Alternatively, the active tablets can be given continuously in selected patients. Combined hormonal contraceptives can reduce endometriosis-associated dyspareunia, dysmenorrhea, and non-menstrual pelvic pain.[69730]
NOTE: For individuals with an intact uterus.
1 tablet (containing norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg with ethinyl estradiol 2.5 mcg OR containing norethindrone acetate 1 mg with ethinyl estradiol 5 mcg) PO once daily. Use lowest effective dose. Reevaluate the appropriateness of hormonal replacement therapy (HRT) at 3 to 6-month intervals.[43360] When treating isolated genitourinary symptoms, consider vaginal topical therapy.[50638] The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) Guidelines support the initiation of HRT around the time of menopause if no contraindications and use is acceptable to the individual patient, as HRT is the most effective treatment for vasomotor and genitourinary symptoms and has been shown to prevent bone loss and fracture.[50638] Early initiation of HRT and continuation of use at until the median age of menopause (52 years) is recommended in women with premature natural or surgically induced menopause. HRT for vasomotor symptoms and/or increased risk for bone loss around the time of menopause may be considered in those women aged younger than 60 years or who are fewer than 10 years from menopause onset.[50638] [52408] For women who initiate HRT more than 10 or 20 years from menopause onset or are aged 60 years or older, the benefit-risk ratio is less favorable due to known risks for HRT and guidelines generally recommend against use in these women. Decisions regarding whether to continue systemic HRT in women older than 60 years of age should be made on an individual basis for quality of life, persistent vasomotor symptoms, or prevention of bone loss and fracture, with consideration given to alternative treatments for prevention of bone loss and other health issues.[50638] [52408]
NOTE: For individuals with an intact uterus.
1 tablet (containing norethindrone acetate 0.5 mg with ethinyl estradiol 2.5 mcg OR containing norethindrone acetate 1 mg with ethinyl estradiol 5 mcg) PO once daily. Use the lowest effective dose. Reassess the appropriateness of hormonal therapy at 3 to 6-month intervals; consider the appropriateness of non-estrogen medications.[43360] In postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density, there is good evidence that standard-dose estrogen therapy reduces the risk for osteoporotic fractures, including hip, spine, and all non-spine fractures; however, estrogens are not generally recommended as first-line prevention due to the known risks of HRT (e.g., thromboembolism, cerebrovascular events) relative to other treatments. Women who need osteoporosis prophylaxis who are younger than 60 years or who are within 10 years of menopause onset may be given consideration for estrogen, based on individual assessment of risk vs. benefit. Beyond the age of 60 years, other agents are preferred due to the known risks of HRT. Consider each woman's net balance of individual benefits and harms. If estrogen with or without a progestin is prescribed, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks. Estrogen therapy should not be used in patients with known osteoporosis; the risks outweigh the moderate benefit seen in postmenopausal women with established osteoporosis.[52408] [62806] [66837] [67122] [67125]
1 tablet (5 mcg ethinyl estradiol with 1 mg norethindrone max dose)/day PO for menopausal symptoms or osteoporosis prevention.
For oral contraception: 1 tablet/day PO as per product prescribed.
1 tablet (5 mcg ethinyl estradiol with 1 mg norethindrone max dose)/day PO for menopausal symptoms or osteoporosis prevention.
For oral contraception: 1 tablet/day PO as per product prescribed.
Not indicated in prepubescent individuals.
Contraindicated for use in patients with known liver impairment or disease.[57612][43360]
These products have not been studied in subjects with renal impairment.[57612][43360]
† Off-label indication
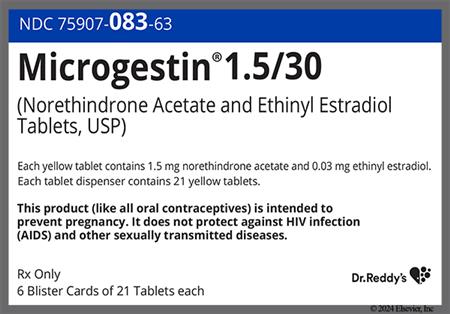

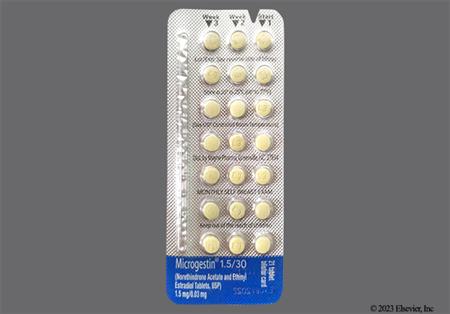
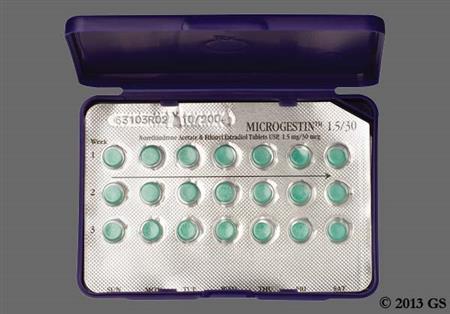


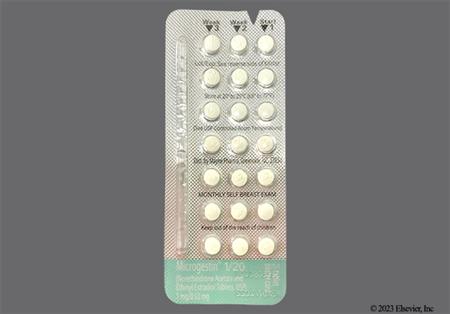




Ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone acetate are an estrogen and progestin, respectively, that are found in combination products for routine contraception or for hormone replacement therapy (HRT). Ethinyl estradiol is a potent, synthetic estrogen. Norethindrone acetate is a first generation oral progestin with moderate androgenic and slight estrogenic activity relative to newer progestins. Norethindrone acetate is known as norethisterone acetate outside the United States. Ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate products are most commonly used as routine oral combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs).[57612][71231] CHCs can be used from the time of menarche to over the age of 40 years, and up until the time of menopause if the individual has no contraindications for use. The choice of a routine hormonal contraceptive is based on the individual's contraceptive needs, underlying medical conditions or risk factors for adverse effects, and individual preferences for use. All CHCs have risks related to venous and arterial thromboembolism, particularly in those who smoke; all CHC labels contain a boxed warning about tobacco smoking. The Centers for Disease Control's U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria describe considerations for risk vs. benefits, including medical conditions or attributes that contraindicate use; these criteria can help practitioners with product selection for individual patients.[48201][66717] The combination of ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate is also found for hormonal replacement therapy (HRT) products for osteoporosis prophylaxis and/or to treat vasomotor and genitourinary symptoms associated with menopause in people with an intact uterus.[43360] A progestin, when added to estrogen hormone replacement, reduces, but does not completely eliminate, the risk for endometrial hyperplasia in such individuals. Boxed warnings for HRT relate to cardiovascular, dementia and cancer risks in the menopausal/postmenopausal population, but these warnings are largely based on use of HRT in women 65 years of age and older, as studied in the Womens Health Initiative trials. Results have consistently shown that estrogen replacement remains the most effective treatment for vasomotor symptoms of menopause and that estrogen replacement helps preserve bone density. Benefits of HRT in early menopause, combined with lower rates of adverse effects and no increase in cardiovascular events or mortality, support initiation of HRT before age 60 years for people without contraindications to use and who have bothersome menopausal symptoms. HRT should be prescribed with an individual assessment of risk vs. benefit, and used for the shortest duration consistent with the treatment goals of the individual.[50638][59154][50675][71260] Ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate CHCs were initially FDA approved in 1968 and HRT products of this combination were first FDA-approved in 1999.
For storage information, see the specific product information within the How Supplied section.
Hazardous Drugs Classification
Hormone replacement tablet (HRT) formulations for menopause (e.g., Femhrt Low Dose 0.5/2.5, Fyavolv, Femhrt 1/5, Jevantique Lo, Jinteli 1/5):
General Information for Oral Combined Hormonal Contraceptives (CHCs)
Oral tablet contraceptive formulations (e.g., Loestrin, Aurovela, Hailey, Larin, Microgestin, Junel):
Orally disintegrating tablet (ODT) contraceptive formulation (e.g., FEMLYV):
General information when initiating routine CHCs: [66717]
Initiating CHCs in an individual not previously taking a CHC: There are options to start taking the first cycle of their CHC.
Switching from a different CHC or other contraceptive methods:
Initiating a CHC in the person with amenorrhea:
Initiating CHCs postpartum:
Initiating CHCs following induced or spontaneous abortion:
A common side effect of oral combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) is breakthrough bleeding and spotting, especially during the first 3 months of CHC use. Menstrual irregularity (5%), oligomenorrhea, and amenorrhea (defined as at least 1 of 6 cycles with a missed withdrawal bleed) are also reported relatively commonly. Menstrual cramps (4.4%) or dysmenorrhea and premenstrual syndrome have also been reported during CHC use. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed dosing schedule, consider the possibility of pregnancy at the time of the first missed period and take appropriate diagnostic measures. If the patient has adhered to the prescribed regimen and misses 2 consecutive periods, rule out pregnancy. A change to another CHC formulation may resolve irregularities that continue to occur during use.[57612] [71231] HORMONE REPLACEMENT (HRT): Amenorrhea often occurs over the course of HRT therapy, with 90% of HRT-treated menopausal patients reporting amenorrhea by the end of year 1 of treatment. Other adverse reproductive effects of HRT that are not as common include changes in or abnormal uterine bleeding or flow, breakthrough bleeding or spotting, increase in size of uterine leiomyomata, ovarian cyst, irregular menstruation, metrorrhagia, menorrhagia, and dysmenorrhea.[43360]
A common adverse reaction reported during norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol CHC product use during clinical trials was breast tenderness (mastalgia) (3.4%). Other breast-related adverse reactions included breast changes (tenderness, pain, breast enlargement, and breast discharge). Lactation suppression has been reported in lactating individuals taking CHCs.[57612] [71231] During trials for use of norethindrone; ethinyl estradiol for hormone replacement (HRT), mastalgia (7.8% to 9%) was most commonly reported. Other non-cancerous adverse breast events included breast tenderness, nipple pain, nipple discharge, galactorrhea, fibrocystic breast changes, breast disorder, and breast enlargement. Lactation suppression may occur with estrogen-based HRT treatment.[43360]
Ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate CHC recipients reported the following adverse vaginal and cervical reactions during clinical trials: vaginal candidiasis (6.1%), bacterial vaginitis (3.1%), and abnormal cervical smear (3.1%). Postmarketing, urogenital adverse events such as fungal infection, vaginal infection, and cystitis-like syndrome have been reported.[57612] [71231] Urogenital symptoms (unspecified) were reported by individuals receiving norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol for hormone replacement (HRT) and postmarketing reports have included vaginitis, vaginal candidiasis, changes in the amount of cervical secretion (leukorrhea) or vaginal discharge, and changes in cervical ectropion.[43360]
Headache (6.3%) was the most common adverse reaction reported with use of the ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate CHC. Discontinue the CHC if new migraines are recurrent, persistent, or severe or if there is an increased frequency or severity of migraines during CHC use (which may be prodromal of a cerebrovascular event). A migraine with aura can increase the risk for cerebrovascular accidents.[57612] [71231] With use of norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol for hormone replacement (HRT), headache (5.7% to 6.2%) was reported during clinical trials and headache and migraine were reported postmarketing.[43360]
Ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate CHCs may cause edema (fluid retention) and weight gain (2%). Postmarketing, both increased and decreased weight have been reported, as well as peripheral edema and changes in appetite (increase or decrease). There is an increased risk of hypertension in CHC users. During clinical trials, 0.4% of ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate CHC users had to discontinue due to increased blood pressure (hypertension). This is consistent with studies which suggest that approximately 41.5 cases of hypertension per 10,000 person-years in the U.S. can be attributed to CHC use. Increased blood pressure is more likely in older people with an extended duration of CHC use. Discontinue the CHC if significant elevation of blood pressure occurs. Blood pressures usually return to normal after discontinuation of therapy, and no difference in the occurrence of hypertension exists among ever- and never-users.[48201] [57612] [71231] An increase in fluid retention may also occur with norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol hormone replacement (HRT). Fluid retention/edema was reported by 4.3% to 4.9% of norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol HRT recipients during clinical trials. Increased blood pressure, edema, and either an increase or decrease in weight have been reported postmarketing. In a few case reports, substantial increases in blood pressure have been attributed to idiosyncratic reactions to estrogens. In a large, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial, a generalized effect of estrogen therapy on blood pressure was not seen. Discontinue the HRT regimen if significant increases in blood pressure occur.[43360]
Combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) such as ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate are associated with an increased risk of thromboembolic and thrombotic disease. The risk for the development of VTE, such as deep venous thrombosis and/or pulmonary embolism is approximately 3 to 6 times greater in CHC users than in nonusers. In several studies, the risk was reported to be substantially higher in smokers compared with nonsmokers, and especially if the smoker was over 35 years of age. The relative risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in people who have predisposing conditions is twice that of those without such medical conditions. The risk of VTE due to CHC use gradually disappears after the CHC is discontinued. VTE risk is highest in the first year of use and when a CHC is started or re-started after a break in use of 4 weeks or more. Estrogens decrease levels of antithrombin-III and increase the production of blood clotting factors VII, VIII, IX and X; risks increase with ethinyl estradiol doses of more than 50 mcg/day. Serious thromboembolic events, such as heart attack or cerebrovascular accidents, are reported rarely in users of CHCs who do not smoke.[48201] Thrombosis/thromboembolism (coronary artery, pulmonary, cerebral, deep vein, mesenteric), angina pectoris, chest pain (unspecified), palpitations, sinus tachycardia, and myocardial infarction have been reported with postmarketing CHC use.[57612] [71231] HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY (HRT): An increased risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), including pulmonary embolism (PE), deep venous thrombosis (DVT), and myocardial infarction (MI) has been reported with estrogen plus progestin HRT. Should any of these events occur or be suspected, discontinue HRT immediately.[43360] In the WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy, a statistically significant 2-fold greater rate of VTE was reported in women receiving estrogen plus progestin HRT compared to women receiving placebo (35 vs. 17 per 10,000 women-years). Statistically significant increases in risk for both DVT (26 vs. 13 per 10,000 women-years) and PE (18 vs. 8 per 10,000 women-years) were also demonstrated. The increase in VTE risk was demonstrated during the first year and persisted.[17825] [27272] Estrogens with or without progestins should not be used for the prevention of cardiac disease or cardiovascular disease (e.g., coronary artery disease). In the Women's Health Initiative (WHI) estrogen-alone substudy, no overall effect on coronary heart disease (CHD) events (defined as non-fatal MI, silent MI, or CHD death) was reported in women receiving estrogen-alone compared to placebo. Subgroup analyses of women 50 to 59 years of age suggest a statistically non-significant reduction in CHD events (CE-alone vs. placebo) in women with less than 10 years since menopause (8 vs. 16 per 10,000 women-years). In the WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy, there was a statistically non-significant increased risk of CHD events (such as myocardial infarction) reported in women receiving daily estrogen plus progestin compared to women receiving placebo (41 vs. 34 per 10,000 women-years). An increase in relative risk was demonstrated in year 1, and a trend toward decreasing relative risk was reported in years 2 through 5.[27272] [17808] Studies have also shown no cardiovascular benefit to the use of estrogens or estrogen-progestin therapy for secondary prevention in women with documented cardiac disease or CHD.[25473] [27270] [43360] In postmarketing use of HRT, deep and superficial venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, thrombophlebitis, thrombosis, chest pain (unspecified), myocardial infarction, irregular heart rate, palpitations, and dyspnea have been reported.[43360]
COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES (CHCs): An increase in both the relative and attributable risks of cerebrovascular events (thrombotic and hemorrhagic strokes with intracranial bleeding) has been shown in users of CHCs such as ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate. The risk is greater among people over 40 years of age, smokers, and in individuals with hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, or obesity. In smokers, the risk for stroke increases with age, particularly in those 35 years of age and older, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. Transient ischemic attack has also been reported postmarketing with CHC use.[48201] [57612] [71231] HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY (HRT): In the WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy, a statistically significant increased risk of thromboembolic stroke was reported in women 50 to 79 years of age receiving daily estrogen plus progestin HRT compared to those in the same age group receiving placebo (33 versus 25 per 10,000 women-years). The increase in risk was demonstrated after the first year and persisted. Cerebrovascular accident (stroke), transient ischemic attack, and hemiparesis have been reported postmarketing. Should a stroke occur or be suspected, the HRT regimen should be discontinued immediately.[43360]
During postmarketing use of ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone CHCs, blurred vision, visual impairment, corneal thinning (keratoconus), and a change in corneal curvature (steepening) have been reported. Retinal thrombosis may occur.[57612] [71231] During postmarketing use of norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol HRT, retinal vascular thrombosis, visual impairment, and intolerance to contact lenses have been reported. Any change in vision or visual acuity should be examined by an ophthalmologist.[43360] Stop the CHC or HRT regimen if there is unexplained loss of vision, proptosis, diplopia, papilledema, or retinal vascular lesions and evaluate for retinal vein thrombosis immediately.[57612] [71231] [43360]
Ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate CHCs have been reported to cause hypersensitivity and dermatologic adverse events. Acne vulgaris (2.7%) is the most common reported dermatologic side effect. Alopecia, rash (generalized and allergic), pruritus, skin discoloration, night sweats, swelling face or lips, hirsutism, skin burning sensation, erythema multiforme, erythema nodosum, hemorrhagic eruption have been reported postmarketing. Anaphylactoid reactions, urticaria, angioedema, and severe reactions with respiratory and circulatory symptoms have also been reported.[57612] [71231] Melasma, a brown patchy skin discoloration, may persist after the CHC is discontinued. Photosensitivity has also been reported rarely with CHC use.[57603] Norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can also cause anaphylactoid reactions, urticaria, and angioedema; severe reactions with respiratory and circulatory symptoms have also been reported. Chloasma or melasma may occur and may persist when the HRT regimen is discontinued. Generalized erythema, erythema multiforme, erythema nodosum, hemorrhagic eruption, loss of scalp hair (alopecia), hirsutism, rash, and pruritus have been reported postmarketing with HRT regimens.[43360]
Nausea (4.6%) was the most common gastrointestinal (GI) side effect occurring during ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate CHC use during clinical trials. Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain have been reported postmarketing. Withhold or permanently discontinue the CHC for persistent or significant elevated hepatic enzymes or if jaundice occurs.[57612] [71231] Rare but serious GI system events which may occur with CHC use include cholestatic jaundice, pancreatitis, peliosis hepatis, Budd-Chiari syndrome, or hepatic vein obstruction. Peliosis hepatis, a very rare consequence of taking estrogens and CHCs, is characterized by the presence of blood-filled spaces.[51257] In rare cases, CHCs can cause benign but dangerous liver tumors. Indirect calculations have estimated the attributable risk of hepatoma to be in the range of 3.3 cases per 100,000 users, a risk that increases after 4 or more years of use. These benign liver tumors can rupture and cause fatal internal bleeding.[57612] Adverse GI events reported during norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol HRT include: nausea, vomiting, cholestatic jaundice, enlargement of hepatic hemangiomas, bloating, abdominal cramps, abdominal pain, increased incidence of gallbladder disease, cholestasis, cholecystitis, and cholelithiasis. If cholestatic jaundice occurs, discontinue the HRT regimen. In women with pre-existing high triglycerides, estrogen therapy may be associated with further elevations of plasma triglycerides leading to pancreatitis.[43360] Numerous cases of bowel ischemia have been reported during combined estrogen and progesterone use; mesenteric vein thrombosis due to hypercoagulability is the proposed mechanism.[57614]
Psychiatric and nervous system disorders reported with ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate CHC regimens include mood swings or emotional lability (2.2%), dizziness, depression, insomnia, anxiety, suicidal ideation, panic attack, and loss of consciousness.[57612] [71231] Psychiatric and nervous system disorders reported with ethinyl estradiol, norethindrone acetate HRT include dizziness, depression, chorea, nervousness or anxiety, mood disturbances, irritability, exacerbation of epilepsy, paresthesias, and insomnia.[43360] Discontinue the CHC or HRT regimen if depression occurs to a significant degree.[43360] [57612] [71231]
Changes in libido (libido increase and libido decrease) have been reported with both ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate CHC and HRT regimens.[43360] [57612] [71231]
Fatigue, malaise, and myalgia have been reported with ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate CHCs.[57612] [71231] Arthralgia, leg muscle cramps, back pain, fatigue, and myalgia have been reported with ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate HRT regimens during postmarketing use.[43360]
Exacerbation of asthma (bronchospasm) has been noted with ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate HRT regimens.[43360]
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT), both estrogen/progestin combination therapy and estrogen alone therapy, fails to prevent mild impaired cognition (memory loss) and is positively associated with the risk of developing dementia in women 65 years and older; do not use HRT to prevent or treat dementia or preserve cognition (memory).[43360] When data from the 2 populations in the WHIMS estrogen-alone and estrogen plus progestin ancillary studies were pooled as planned in the WHIMS protocol, the reported overall relative risk for probable dementia was 1.76 (95% CI 1.19 to 2.60, p = 0.005). Since both ancillary studies were conducted in women 65 to 79 years of age, it is unknown whether these findings apply to younger postmenopausal women.[27451] [32126] [50638] In the Women’s Health Initiative Memory Study (WHIMS) estrogen plus progestin ancillary study, a population of 4,532 postmenopausal women 65 to 79 years of age was randomized to daily estrogen plus progestin or placebo. After an average follow-up of 4 years, 40 women in the estrogen plus progestin group and 21 women in the placebo group were diagnosed with probable dementia. The relative risk of probable dementia for estrogen plus progestin vs. placebo was 2.05 (95% CI, 1.21 to 3.48). The absolute risk of probable dementia for estrogen plus progestin vs. placebo was 45 vs. 22 cases per 10,000 women-years.[27451] In the WHIMS estrogen-alone ancillary study of WHI, a population of 2,947 hysterectomized women 65 to 79 years of age was randomized to daily estrogen-alone or placebo. After an average follow-up of 5.2 years, 28 women in the estrogen-alone group and 19 women in the placebo group were diagnosed with probable dementia. The relative risk of probable dementia for estrogen-alone vs. placebo was 1.49 (95% CI, 0.83 to 2.66). The absolute risk of probable dementia for estrogen-alone versus placebo was 37 vs. 25 cases per 10,000 women-years.[32126]
Aggravation of porphyria has been noted with estrogens, including ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate CHC and HRT regimens.[43360] [57612] [71231]
Combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) can alter certain laboratory tests. Impaired glucose tolerance and hypertriglyceridemia may occur. Those with hypertriglyceridemia, or a family history thereof, may have an increase in serum triglyceride concentrations when using CHCs which may increase the risk of pancreatitis. Estrogens may increase the serum concentrations of thyroxine-binding globulin, sex hormone-binding globulin, and cortisol-binding globulin.[57612] [71231] Ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate HRT may also reduce carbohydrate tolerance and cause abnormal or increased blood glucose (hyperglycemia), hypocalcemia, and increased triglycerides (hypertriglyceridemia).[43360]
In women with a history of cardiovascular disease, the use of estrogen and progestin combination therapy (e.g., ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate) increases the risk of developing urinary incontinence. Patients in the HERS study who did not have urinary incontinence prior to the studies initiation were observed to determine if hormone replacement therapy was helpful in preventing urinary incontinence. The study found that women who received estrogen/progestin therapy were almost twice as likely as patients receiving placebo to develop urge incontinence and 3 times as likely to develop stress incontinence after 1 year of treatment. At 4 years, the effect of hormone replacement therapy became even more pronounced, increasing the risk to 3.23 for urge incontinence and to 4.81 for stress incontinence. The applicability of these findings to women who use estrogen alone is unclear.[27457]
Some women taking estrogens or oral contraceptives notice tenderness, swelling, or minor bleeding of their gums, which may lead to gingivitis. Proper attention to oral care and regular dental visits during ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate therapy are recommended.
The issue of hormonal influences on the development of cancers has been widely researched for many decades. The risks of various cancers for combined oral contraceptive (COC) use in premenopausal women differ from the risks associated with hormone replacement therapy (HRT) in postmenopausal women. HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY POSTMENOPAUSE: Numerous epidemiologic studies have examined the effects of estrogen and estrogen-progestin hormone replacement therapy (HRT) on the development of new primary malignancy (e.g., breast cancer, endometrial cancer, ovarian cancer) in postmenopausal women. The Women's Health Initiative (WHI) estrogen plus progestin study reported increased risks of invasive breast cancer in patients taking combined estrogen-progestin HRT vs. placebo. The potential risk of breast cancer may increase with longer duration of use. Due to breast cancer and other cancer risks, combined HRT should be prescribed at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.[43360] [27272] [32125] [27273] [50638] There is an association of unopposed estrogen therapy and endometrial cancer in women with an intact uterus. Adding a progestin to estrogen therapy has been shown to reduce, but not eliminate, the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, which may be a precursor to endometrial cancer. Clinical surveillance of all women using estrogen-alone or estrogen plus progestin therapy is important. Adequate diagnostic measures, including directed or random endometrial sampling when indicated, should be undertaken to rule out malignancy in postmenopausal women with undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal vaginal bleeding. The reported endometrial cancer risk among unopposed estrogen users is about 2- to 12-times greater than in non-users, and appears dependent on duration of treatment and on estrogen dose. Most studies show no significant increased risk associated with use of estrogens for less than 1 year. The greatest risk appears associated with prolonged use, with increased risks of 15- to 24-fold for 5 to 10 years or more, and this risk has been shown to persist for at least 8 to 15 years after estrogen therapy is discontinued. There is no evidence that the use of natural estrogens results in a different endometrial risk profile than synthetic estrogens of equivalent estrogen dose. Among combined estrogen/progestin HRT users, roughly 10% will have some endometrial thickening. Postmarketing reports of endometrial hyperplasia have been reported in women receiving combined estrogen/progestin HRT; however, the incidence of endometrial hyperplasia is estimated to be 1% or less in these patients.[43360] [50638] [23505] [27272] Women who used HRT for menopausal symptoms also had an increased risk for ovarian cancer, but data are still uncertain if risk is associated with a specific duration of use. The contraindications and precautions sections for the ethinyl estradiol-norethindrone acetate HRT product labels more fully discuss the data and what is known about HRT use with respect to risks for various cancers.[43360] [27272] [32125] [27273] [50638] COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES (CHCs): Most studies have been performed with combined oral contraceptives, and the risks related to CHCs, regardless of route of administration, are thought to be similar. In general, the data suggest an increased risk of cervical cancer among CHC users, with a decreased risk for endometrial and ovarian cancers. Epidemiology studies have not found a consistent association between use of CHCs and breast cancer risk. Studies do not show an association between ever (current or past) use of CHCs and risk of breast cancer. However, some studies report a small increase in the risk of breast cancer among current or recent users (less than 6 months since last use) and current users with longer duration of COC use.[57612] [62904] Several large, well-designed observational studies have provided data regarding the risk of breast cancer with CHC use.[27233] [24750] [27234] Breast cancers diagnosed in current or previous CHC users tend to be less advanced clinically than in never-users. The risk of breast cancer is only slightly increased in current and recent CHC users (i.e., within 10 years); however, 10 years after CHC cessation, the risk of breast cancer appears to be similar to that in those patients that have never used CHCs.[62647] From one large study published in 2017, the risk of breast cancer was higher among women who currently or recently used contemporary CHCs than among women who had never used CHCs, and this risk increased with longer durations of use; however, absolute increases in risk were small. The absolute risk of breast cancer associated with any CHC use was 13 per 100,000 women-years, which corresponds to 1 extra case of breast cancer for every 7,690 CHC users in 1 year.[62904] Moreover, the same study data suggest that any increased risk of breast cancer usually disappears rapidly after an interruption in the use of CHCs.[62904] There continues to be controversy regarding the risk of CHC use in women with a family history of breast cancer (e.g., BRCA mutations). However, evidence does not suggest that the increased risk for breast cancer among women with either a family history of breast cancer or breast cancer susceptibility genes is modified by the use of CHCs.[48201] Patients should be instructed to perform monthly self-breast examination and report any breast changes, lumps, or discharge to their health care professional. If breast cancer is suspected, CHCs should be discontinued.[57612] Some studies suggest that CHC use has been associated with an increase in the risk of cervical cancer or intraepithelial neoplasia; however, such findings may be due to differences in sexual behavior, presence of the human papillomavirus (HPV) and other factors. HPV is thought to be the cause of more than 90% of all cervical cancers, although hormonal factors may influence risk. The relative risk of invasive cervical cancer of 1.37 after 4 years of use; relative risk increased to 1.6 after 8 years of CHC use. Because a potential for cervical dysplasia may exist, regularly evaluate patients taking CHCs via cervical cytology screening as recommended per standards of care.[62647] A meta-analysis of 10 studies indicated significant trends for a reduced risk for endometrial and ovarian cancer with increased duration of CHC use. Risk of endometrial or ovarian cancers may be reduced by up to 60% with 4 or more years of use.[25198] Data suggest CHCs do not protect against hereditary forms of ovarian cancer (e.g., women who carry BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene alterations).[25199] Studies have shown an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in long-term (more than 8 years) CHC users. However, these cancers are rare in the U.S., and the attributable risk (the excess incidence) of liver cancers in CHC users approaches less than 1 per million users.[62647] [57612] [71231]
Use of norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol contraceptive products, as with other contraceptive steroids, may result in clinical changes that influence the results of certain laboratory tests, such as coagulation factors, lipids, glucose tolerance, and binding proteins. Specific laboratory test interference has not been reported.[57612]
The coadministration of certain medications may lead to harm and require avoidance or therapy modification; review all drug interactions prior to concomitant use of other medications.
This medication is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to it or any of its components.
Combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs), such as ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate, do not protect against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection or other sexually transmitted disease. Patients infected with HIV or with known acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) should be aware that the use of a CHC will not prevent the transmission of HIV or other sexually transmitted diseases to their partner(s).[57612]
COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES (CHCs): CHCs are contraindicated in people with a current or past history of cerebrovascular disease (including stroke), coronary artery disease, or thromboembolism [including coronary thrombosis, myocardial infarction (MI), thrombophlebitis, thromboembolic disease, or valvular heart disease with complications]. CHCs have been associated with thromboembolic disease such as deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). CHCs are also generally contraindicated in thrombogenic valvular or heart rhythm diseases (e.g., atrial fibrillation or subacute bacterial infective endocarditis with valvular disease, atrial fibrillation), or known inherited or acquired hyper-coagulopathic thrombophilia (e.g., protein S deficiency, protein C deficiency, Factor V Leiden, prothrombin G20210A mutation, antithrombin deficiency, antiphospholipid antibodies). People with a history of retinal thrombosis should not receive CHCs due to the potential risk of vision loss should retinal thrombosis occur due to the CHC. Because tobacco smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events and thromboembolism, CHC recipients are strongly advised not to smoke. Risk is especially high for heavy smokers (15 or more cigarettes per day) over 35 years of age; therefore, CHCs are considered contraindicated for tobacco smokers more than 35 years of age. Due to association of estrogen dosage with thromboembolic risk, CHCs containing 50-mcg/day ethinyl estradiol should not be used unless medically indicated. In addition, certain progestins may increase thromboembolic risk. The overall risk of venous thromboembolism in oral CHC users has been estimated to be 3 to 9 per 10,000 woman-years. Preliminary data from a large, prospective cohort safety study suggests that the risk is greatest during the first 6 months after initially starting CHC therapy or restarting (following a break from therapy 4 weeks or more) with the same or different combination product. The risk of arterial thromboses, such as stroke or MI, is especially increased in those with other risk factors, such as pre-existing high blood pressure, renal disease, elevated lipids or cholesterol, diabetes with vascular disease, or if morbidly overweight. After a CHC is discontinued, the risk of thromboembolic disease due to CHCs gradually disappears. CHCs are also associated with increases in blood pressure (BP), and CHCs are considered contraindicated in those with uncontrolled hypertension (e.g., persistent blood pressure values of 160 mmHg systolic or 100 mmHg diastolic or greater) or hypertension with vascular disease. For all CHC users, including those with well-controlled hypertension, monitor BP at routine visits and stop the CHC if BP rises significantly. An increase in BP is more likely in older CHC users with an extended duration of use. The effect of CHCs on BP may vary according to the progestin in the CHC. CHCs may also cause fluid retention, and individuals predisposed to complications from edema, such as those with chronic kidney disease (CKD) or cardiac disease should be closely monitored.[57612] [71231] [48201] HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY (HRT): Due to the potential for serious cardiovascular events, estrogen-containing hormonal replacement therapy (HRT) products are contraindicated in people with active thromboembolism (e.g., DVT or PE) or a history of these conditions as well as those with active arterial thromboembolic disease (e.g., stroke and myocardial infarction), or a history of these conditions. Increased risks of PE, DVT, stroke, and MI are reported with estrogen plus progestin HRT. Increased risks of stroke and DVT are reported with estrogen-alone therapy. Immediately discontinue HRT if any of these events occur or are suspected.[43360] Estrogens with or without progestins should not be used for the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Individuals with certain risk factors for arterial vascular disease (e.g.,cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes, tobacco smoking, hypercholesterolemia, and morbid obesity) and/or venous thromboembolism (VTE) (e.g., personal history or family history of VTE, obesity, or systemic lupus erythematosis) should be monitored and managed appropriately during HRT use.[43360] Monitor blood pressure in all postmenopausal individuals receiving HRT and especially in those with pre-existing hypertension; in a few case reports, substantial increases in blood pressure have been attributed to idiosyncratic reactions to estrogen HRT therapy. In a large, randomized, placebo controlled clinical trial, a generalized effect of estrogens on blood pressure was not seen. Estrogen-based HRT may cause some degree of fluid retention. Individuals with conditions that might be influenced by this factor, such as cardiac dysfunction, warrant careful observation when estrogens are prescribed.[43360] [50638]
Major surgery can increase the risk for thromboembolism from combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) or estrogen-based hormone replacement therapy (HRT). CHCs and HRT are contraindicated when there is major surgery with prolonged immobility. If feasible, discontinue the CHC or HRT at least 4 weeks before and for 2 weeks after major surgery or other planned procedure known to have an elevated risk of thromboembolism, and during and following any prolonged immobility.[43360] [57612] [71231]
COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES: Because of the increased potential for embolic risk, combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) are contraindicated in people who currently have diabetes mellitus and are more than 35 years of age, diabetes mellitus with hypertension or with vascular disease or end-organ damage, or diabetes mellitus of greater than 20 years duration. People with diabetes mellitus should be observed for changes in glucose tolerance when initiating or discontinuing CHCs, since estrogens may exacerbate diabetes. Altered glucose tolerance secondary to decreased insulin sensitivity has been reported.[57612] [71231] HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY (HRT): Patients with diabetes mellitus should be observed for changes in glucose tolerance when initiating or discontinuing estrogen-based HRT, since estrogen therapy may exacerbate diabetes. Altered glucose tolerance secondary to decreased insulin sensitivity has been reported.[43360]
People who are being treated for dyslipidemia should be followed closely if they elect to use combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs). Some progestogens may elevate LDL levels and may render the control of hyperlipidemia more difficult. Those with hypertriglyceridemia, or a family history thereof, may be at an increased risk of pancreatitis when using CHCs.[57612] [71231] Changes in cholesterol and triglyceride levels may also occur with estrogen-based hormone replacement therapy. In people with pre-existing hypertriglyceridemia, estrogen HRT may be associated with elevations of plasma triglycerides leading to pancreatitis. Discontinue the HRT regimen if pancreatitis occurs.[43360]
Exogenous estrogens may exacerbate symptoms of angioedema in individuals with hereditary angioedema. Consider whether the benefits of estrogen therapy outweigh the risks in such individuals. [43360] [57612] [71231]
COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES (CHCs): CHC products are contraindicated in people with migraine with aura or other headache that is accompanied by focal neurological symptoms. CHCs are also contraindicated in people more than 35 years of age with migraine headaches of any type. The onset or exacerbation of migraine or development of headache with a new pattern which is recurrent, persistent, or severe requires discontinuation of CHCs and evaluation of the cause. A migraine with focal neurologic visual changes should be medically evaluated, as such changes may indicate cerebrovascular events.[57612] [71231] HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY (HRT): Estrogen-based hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may cause an exacerbation of migraine and should be used cautiously in people with this condition. Discontinue the HRT regimen pending examination if there is a migraine with focal neurologic or visual changes.[43360]
Estrogens, such as those in combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) regimens, can increase the curvature of the cornea. CHC recipients who wear contact lenses who develop visual changes or changes in lens tolerance should be assessed by an ophthalmologist.[57612] [71231]
COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES: Combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) are contraindicated for use in people with acute or chronic hepatic disease with abnormal liver function, such as hepatic failure, acute hepatitis or decompensated hepatic cirrhosis. Other liver conditions for which estrogen-containing birth control is inappropriate include Budd-Chiari syndrome, a liver transplant that is not working well, or benign or cancerous hepatic tumors. In general, CHCs are also contraindicated in those with a history of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy or a history of significant adverse event(s) associated with previous use of a hormonal contraceptive. Discontinue the CHC if jaundice or cholestasis develops during use. Acute or chronic disturbances of liver function may necessitate CHC discontinuation until markers of liver function return to normal and CHC causation has been excluded. Patients with hepatitis C infection who are being treated with ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, are also contraindicated to receive CHCs due to a risk for elevated hepatic enzymes and hepatotoxicity. Discontinue CHCs prior to starting hepatitis C therapy with these antiviral regimens; a CHC can be restarted approximately 2 weeks following completion of these hepatitis C combination drug regimens. Estrogen therapy may cause an exacerbation of porphyria and should be used with caution in people with this condition.[57612] [71231] [48201] [70437] HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY (HRT): Estrogens and progestins in HRT regimens may be poorly metabolized in people with impaired liver function and are contraindicated in people with hepatic failure, impairment, or disease. For people with a history of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy or a history of significant adverse event(s) associated with previous use of an estrogen, such as cholestatic jaundice, use estrogens with caution. If there is a recurrence of cholestatic jaundice, discontinue the HRT regimen. Estrogen HRT therapy may cause an exacerbation of porphyria or hepatic hemangioma and should be used with caution in people with these conditions.[25473] [43360] Liver disease guidelines recommend that menopausal estrogen-based HRT not be used in people with the following conditions: decompensated liver function, Budd-Chiari syndrome, or hepatocellular adenoma (benign liver tumor).[72725]
COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES: Use of combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) is contraindicated in people with a benign or malignant liver tumor, such as hepatic adenoma or hepatocellular cancer. Benign hepatic adenomas are associated with CHC use, although the incidence of these benign tumors is rare. The attributable risk (the excess incidence) is 3.3 cases/100,000 CHC users. Rupture of hepatic adenomas may cause death through intra-abdominal hemorrhage. Studies have shown an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma in long-term (more than 8 years) CHC users. However, these cancers are extremely rare in the U.S. and the attributable risk of liver cancers in CHC users is less than 1 per million CHC users. Estrogens may cause an exacerbation of hepatic hemangiomas and should be used with caution in people with this condition.[57612] [71231] [48201] [70437]
COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES (CHCs): Given the increased prevalence of hypercoagulable states in people with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), consider the thromboembolic risk versus the benefit of combined hormonal contraceptive (CHC) use. Avoid CHCs in SLE patients with a history of venous or arterial thrombosis or the presence of a hypercoagulable state (antiphospholipid antibodies and lupus anticoagulant). If CHCs are initiated in SLE patients without hypercoagulable states, choose a low-dose estrogen contraceptive (e.g., ethinyl estradiol 35 mcg per day or less); consider use of a progestin-only contraceptive. CHCs have also been reported to induce, unmask, or exacerbate SLE; more data are needed.[31435] [48201] HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY (HRT): Individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) may have an increased risk for thromboembolism and should be managed appropriately when estrogen hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used. Estrogen HRT may cause an exacerbation of SLE and should be used with caution in people with this condition.[43360]
Mood disorders, like depression, may be aggravated in women taking combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs). Data regarding the association of CHCs with onset of depression or exacerbation of existing depression are limited. If significant depression occurs, norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol products should be discontinued.[57612] [71231] Mood disorders, like depression, may be aggravated in women taking estrogen-based hormone replacement therapy (HRT); if significant depression occurs, HRT should be discontinued.[43360]
COMBINED HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION: Combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) are contraindicated in people with a current diagnosis of, or history of, breast cancer, endometrial cancer, or other known or suspected estrogen-dependent tumor, as such tumors may be hormonally-sensitive. CHCs are also contraindicated in people with abnormal uterine bleeding; evaluate such patients before use to determine if a contraindication to CHC use exists. Clinical surveillance of all individuals using CHCs is important; perform breast examinations or mammography, pelvic examination, and other diagnostic or screening tests, such as cervical cytology (pap smears), as clinically indicated or as generally recommended based on age, risk factors, and other individual needs.[57612] [71231] [48201] ESTROGEN-BASED HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY (HRT): Estrogen-based hormone replacement therapy (HRT) products are contraindicated in people with undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding or a history of or known/suspected breast cancer, endometrial cancer, or other estrogen-dependent tumor, which may be hormonally-sensitive. There is an increased risk of endometrial cancer in a person with a uterus who uses unopposed estrogens. Adding a progestin to estrogen HRT has been shown to reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, which may be a precursor to endometrial cancer. Adequate diagnostic measures, including directed or random endometrial sampling when indicated, should be undertaken to rule out malignancy in postmenopausal women with undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal genital bleeding. Studies suggest that the use of estrogen-progestin HRT in postmenopausal women increases the risk for invasive breast cancer. The use of estrogen-alone and estrogen plus progestin HRT has been reported to result in an increase in abnormal mammograms, requiring further evaluation. All people taking estrogen with or without a progestin as HRT should receive an annual clinical breast examination, perform monthly self-examinations, and have regular mammograms as recommended by their health care professional based on patient age, risk factors, and prior mammogram results.[43360] While estrogen therapy is rarely used for the palliative treatment of advanced breast cancer, estrogen HRT use may lead to severe hypercalcemia in patients with breast cancer and bone metastases. If hypercalcemia occurs, use of HRT should be stopped and appropriate measures taken to reduce the serum calcium level.[43360]
Avoid combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) in persons with a history of chloasma gravidarum or increased sensitivity to sun and/or ultraviolet radiation exposure. Chloasma (melasma) may occur with CHC use, especially in people with a history of chloasma gravidarum.[57612] [71231]
Because estrogens influence the growth of endometrial tissues, use estrogen regimens for hormone replacement therapy (HRT) cautiously in those with endometriosis or uterine leiomyoma (uterine fibroids). A few cases of malignant transformation of residual endometrial growths have been reported in people treated post-hysterectomy with estrogen-alone HRT therapy. For individuals known to have residual endometriosis post-hysterectomy, consider the addition of a progestin to estrogen HRT, such as the use of norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol products, to reduce the risk of endometrial tissue growth.[43360]
Studies suggest a small increased relative risk of developing gallbladder disease among combined hormonal contraceptive (CHC) users.[48201] [57612] [71231] HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY: Estrogens have been reported during trials to increase the risk of gallbladder disease (e.g., cholestasis, cholelithiasis and cholecystitis) by roughly 2- to 4-fold in postmenopausal women.[43360]
The estrogen component of combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) or hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may raise the serum concentrations of thyroid-binding globulin, sex hormone-binding globulin, and cortisol-binding globulin. Doses of thyroid hormone replacement for hypothyroidism may need to be increased during CHC or HRT use, as indicated by clinical and laboratory monitoring of the individual. Cortisol replacement therapy (e.g., corticosteroid therapy) may also need adjusted for some patients.[43360] [57612] [71231]
Preexisting morbid obesity is one factor that may increase cardiovascular or thromboembolic risks associated with combination hormonal contraceptives (CHCs). Consider the presence of obesity and other underlying risk factors that may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease or thromboembolism, particularly for people over 35 years of age.[57612] [71231] Limited literature suggests that the effectiveness of some hormonal contraceptive formulations might decrease with increasing body mass index (BMI). However, the evidence is conflicting; there are also data to suggest that the efficacy of most CHC products (with a few known exceptions) does not seem to be compromised in those who are overweight.[48201] [66895] The efficacy of the norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol oral disintegrating tablet CHC (FEMLYV) was not studied in those with a BMI of more than 35 mg/m2.[71231]
Estrogen hormone replacement therapy (HRT), such as selected norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol products, should be used with caution in people with hypoparathyroidism as estrogen-induced hypocalcemia may occur.[43360]
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) with norethindrone acetate; ethinyl estradiol should not be used for the prevention of dementia. HRT, both estrogen-progestin combination therapy and estrogen alone therapy, fails to prevent mild cognitive impairment (memory loss) and increases the risk of dementia in females 65 years of age and older.[43360] Administration of HRT should generally be avoided in people 65 years of age and older, and HRT should not be used to prevent or treat dementia or preserve cognition (memory). Overall risk vs. benefit should be considered along with the goals of use of HRT for the individual patient when considering whether to continue HRT in a geriatric woman over 65 years of age.[27451] [32126] [50638] According to the Beers Criteria, oral, topical patch, or other systemic forms of estrogens (with or without progestins), are considered potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) for use in geriatric adults and should be avoided due to evidence of carcinogenic potential (i.e., breast and endometrium) and lack of cardiovascular or cognitive protective effects. Avoid oral or transdermal estrogen in elderly adult women with any type of urinary incontinence due to lack of efficacy for this condition. The use of vaginal estrogens is acceptable for the management of dyspareunia and vaginal/vulvar symptoms.[63923]
Estrogens and/or progestins may cause some degree of fluid retention. Monitor any person receiving hormone replacement therapy (HRT) with a condition(s) that might predispose her to fluid retention, such as renal failure or renal impairment. Discontinue HRT if there is medically-concerning fluid retention. Estrogen-based HRT may cause an exacerbation of asthma or epilepsy (seizure disorder). Consider whether the benefits of estrogen-based HRT therapy outweigh the risks in people with such conditions.[43360]
Discontinue combined hormonal contraceptive (CHC) products if pregnancy is detected as there is no reason to continue CHCs during pregnancy. Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or nongenital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects) following exposure to CHCs before conception or during early pregnancy. The administration of CHCs to induce withdrawal bleeding should not be used as a test for pregnancy. CHCs should not be used during pregnancy to treat threatened or habitual abortion. For any CHC user who has missed 2 consecutive periods, pregnancy should be ruled out before continuing CHC use. If the CHC user has not adhered to the prescribed schedule, consider the possibility of pregnancy at the first missed period; discontinue the CHC until pregnancy is ruled out.[30858] [57612] [71231] Do not use hormone replacement therapy (HRT) during pregnancy as HRT products for menopausal symptoms are not indicated for use in pregnancy. Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or nongenital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects) following exposure to CHCs before conception or during early pregnancy.[43360]
Product labels for combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) recommend avoidance if possible during breast-feeding until the lactating individual has completely weaned their child. Small amounts of hormonal contraceptive steroids (estrogens and progestins) have been identified in human milk and a few reports of effects on the infant exist, including jaundice and breast enlargement.[57612] [71231] The U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria (USMEC) state that CHCs should not be used during the first 4 weeks after delivery because of concerns about the potential effects of estrogen on breast-feeding performance during the establishment of lactation. If a patient is breast-feeding and begins taking a CHC 4 to 6 weeks after delivery, the breastfed infant should be monitored for appetite changes, hormonal side effects, and proper weight gain/growth.[48201] One study found that low-dose CHCs (e.g., 10 mcg per day ethinyl estradiol) may not adversely affect lactation.[48200] However, a systematic review concluded that the available evidence, even from randomized controlled trials, is limited and of low quality; proper trials are needed.[48202] The World Health Organization (WHO) Contraceptive Criteria has recommendations that are more restrictive than USMEC; the WHO criteria state CHCs should not be used in breast-feeding individuals before 42 days after birth and that the disadvantages of CHC use generally outweigh the advantages between 6 weeks and 6 months after birth for individuals who are breast-feeding.[48204] Alternate contraceptive agents to consider for the breast-feeding individual include non-hormonal contraceptive methods (e.g., copper IUD, barrier methods, spermicides) and progestin-only contraceptives (e.g., medroxyprogesterone contraceptive injections, norgestrel oral contraceptive, levonorgestrel IUDs).[48201] HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY (HRT): Use estrogen-based HRT products with caution during breast-feeding. Estrogen administration has been shown to decrease the quantity and quality of the breast milk and detectable amounts of drug have been identified in the milk. A reduction in lactation can occur at any time but is less likely to occur once breast-feeding is well-established.[43360]
The U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria state to avoid combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) during the first 3 weeks postpartum because of the increased risk for venous thromboembolism in the early postpartum period. Postpartum individuals with additional risk factors for venous thromboembolism (VTE) (e.g., 35 years of age or older, previous VTE, thrombophilia, immobility, transfusion at delivery, peripartum cardiomyopathy, obesity with a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or more, postpartum hemorrhage, post-cesarean delivery, preeclampsia, or tobacco smoking) should generally not use CHCs until at least 6 weeks after delivery. CHCs may be used after 6 weeks postpartum without restriction if no other contraindications to CHCs exist, as postpartum thromboembolism risk returns to baseline.[48201]
The net effects of the combination of ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate combinations are dependent on the age and hormonal status of the treated patient (i.e., pre- or post-menopausal) and the dosage of the combination administered.
Progestins produce similar endometrial changes to those of the naturally occurring hormone progesterone. Progestin compounds enhance cellular differentiation and generally oppose the actions of estrogens by decreasing estrogen receptor levels, increasing local metabolism of estrogens to less active metabolites, or inducing gene products that blunt cellular responses to estrogen. Progestins exert their effects in target cells by binding to specific progesterone receptors that interact with progesterone response elements in target genes. Progesterone receptors have been identified in the female reproductive tract, breast, pituitary, hypothalamus, bone, skeletal tissue and central nervous system. In menopausal individuals taking estrogen replacement, the addition of a progestin converts a proliferative endometrium into a secretory one, thus reducing endometrial hyperplasia and the risk of endometrial carcinoma.[43360][50638]
Ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate is administered orally as either a contraceptive or hormone replacement therapy. The volume of distribution of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol ranges from 2 to 4 L/kg. The distribution of exogenous estrogens is similar to that of endogenous estrogens. Estrogens are widely distributed in the body and are generally found in higher concentrations in the sex hormone target organs. Plasma protein binding of both steroids is extensive (more than 95%). Norethindrone binds to both albumin and sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), whereas ethinyl estradiol binds only to albumin. Although ethinyl estradiol does not bind to SHBG, it induces SHBG synthesis. Norethindrone undergoes extensive biotransformation, primarily via reduction followed by sulfate and glucuronide conjugation. Hydroxylation of norethindrone is mostly mediated by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C19. A small amount of norethindrone acetate is metabolically converted to ethinyl estradiol. Ethinyl estradiol is also extensively metabolized both by oxidation and by conjugation with sulfate and glucuronide. The primary oxidative metabolite of ethinyl estradiol is 2-hydroxy ethinyl estradiol formed by CYP3A4. Hydroxylation of ethinyl estradiol appears to be mediated to a minor extent by CYP2C9. Part of the first-pass metabolism of ethinyl estradiol is believed to occur in gastrointestinal mucosa. Ethinyl estradiol undergoes some enterohepatic circulation. Glucuronidation of ethinyl estradiol is primarily catalyzed by UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) in the liver. Sulfotransferase 1E1 (SULT1E1) is suggested to play a predominant role (70% or more) in the sulfation of ethinyl estradiol in the intestine and liver. For both hormones, most metabolites in the circulation are sulfates with glucuronides accounting for most of the urinary metabolites. Norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol are excreted in both urine and feces primarily as metabolites. Estradiol, estrone, and estriol are excreted in the urine along with these glucuronide and sulfate conjugates. Plasma clearance values for norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol are similar (approximately 0.4 L/hour/kg). Elimination half-lives of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol contraceptive products following administration are approximately 10 hours and 18 hours, respectively. Steady-state elimination half-lives of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol following administration of norethindrone-ethinyl estradiol tablets for HRT are approximately 13 hours and 24 hours, respectively. It is the prolonged biologic effects of these hormones that allow for once-daily administration.[43360][57612][71231][70622]
Affected cytochrome P450 isoenzymes and drug transporters: CYP3A4, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, P-glycoprotein (P-gp), UGT1A1, SULT1E1
Since ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone are partially metabolized by CYP3A4, interactions with drugs that are inhibitors or inducers of CYP3A4 are possible.[43360][57612][71231] Drugs or herbal products that induce CYP3A4 may decrease the efficacy of CHC or HRT treatment or may increase the risk for breakthrough bleeding. For CHCs, avoiding concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inducer is recommended to mitigate the risk of potential contraceptive failure. Moderate and weak inducers may also affect progestin and estrogen exposures depending on the agent. Conversely, exposures of ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone are generally increased by up to 50% when coadministered with moderate or strong inhibitors of CYP3A4.[70622] Ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone are substrates of the drug transporter P-gp, but data suggest that clinical drug interactions are not expected with P-gp inhibitors or inducers.[60859][70622] There are not enough data to assess the effects of modulation of UGT1A1 or SULT1E1 on hormone concentrations in these products.[70622] Ethinyl estradiol has been shown to induce lamotrigine glucuronidation.[43360]
Contraceptive tablets and orally disintegrating tablet (ODT): Norethindrone acetate appears to be completely and rapidly deacetylated to norethindrone after oral administration, since the disposition of norethindrone acetate is indistinguishable from that of orally administered norethindrone. Norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol are subject to first-pass metabolism after oral dosing, resulting in an absolute bioavailability of approximately 64% for norethindrone and 43% for ethinyl estradiol. No clinically significant differences in pharmacokinetics of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol ODT were observed following administration of a high-fat meal in healthy premenopausal subjects.[57612][71231]
Tablets for hormone replacement therapy (HRT): Norethindrone acetate is completely deacetylated to norethindrone after oral administration, and the disposition of norethindrone acetate is indistinguishable from that of orally administered norethindrone. Maximum plasma concentrations of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol generally occur 1 to 2 hours postdose. Both drugs are subject to first-pass metabolism after oral dosing, resulting in an absolute bioavailability of approximately 64% for norethindrone and 55% for ethinyl estradiol. Bioavailability of norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol HRT tablet is similar to that from an oral solution for norethindrone and slightly less for ethinyl estradiol. Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, average steady-state concentrations (Css) of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol for norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol 1/5 tablets are estimated to be 2.6 ng/mL and 11.4 pg/mL, respectively. Css values of norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol for norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol 0.5/2.5 tablets are estimated to be 1.1 ng/mL and 5.4 ng/mL, respectively. Administration of norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol HRT tablets with a high fat meal decreases rate but not extent of ethinyl estradiol absorption. The extent of norethindrone absorption is increased by 27% following administration of norethindrone acetate and ethinyl estradiol tablets with food.[43360]
Ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate combinations have not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment. However, steroid hormones may be poorly metabolized in people with impaired liver function.[57612][71231][43360]
The pharmacokinetics of ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate products have not been studied in subjects with renal impairment.[57612][71231][43360] In premenopausal women with chronic renal failure undergoing peritoneal dialysis who received multiple doses of an oral contraceptive containing ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone, plasma ethinyl estradiol concentrations were higher and norethindrone concentrations were unchanged compared to concentrations in premenopausal women with normal renal function.[57612]
The effect of race on the disposition of ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone acetate contraceptive tablets has not been evaluated.[57612]
Pharmacokinetic, safety and efficacy data have not been fully evaluated for the ethinyl estradiol; norethindrone contraceptive orally disintegrating tablet for individuals with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 35 kg/m2.[71231]
Discontinue combined hormonal contraceptive (CHC) products if pregnancy is detected as there is no reason to continue CHCs during pregnancy. Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or nongenital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects) following exposure to CHCs before conception or during early pregnancy. The administration of CHCs to induce withdrawal bleeding should not be used as a test for pregnancy. CHCs should not be used during pregnancy to treat threatened or habitual abortion. For any CHC user who has missed 2 consecutive periods, pregnancy should be ruled out before continuing CHC use. If the CHC user has not adhered to the prescribed schedule, consider the possibility of pregnancy at the first missed period; discontinue the CHC until pregnancy is ruled out.[30858] [57612] [71231] Do not use hormone replacement therapy (HRT) during pregnancy as HRT products for menopausal symptoms are not indicated for use in pregnancy. Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or nongenital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects) following exposure to CHCs before conception or during early pregnancy.[43360]
Product labels for combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) recommend avoidance if possible during breast-feeding until the lactating individual has completely weaned their child. Small amounts of hormonal contraceptive steroids (estrogens and progestins) have been identified in human milk and a few reports of effects on the infant exist, including jaundice and breast enlargement.[57612] [71231] The U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria (USMEC) state that CHCs should not be used during the first 4 weeks after delivery because of concerns about the potential effects of estrogen on breast-feeding performance during the establishment of lactation. If a patient is breast-feeding and begins taking a CHC 4 to 6 weeks after delivery, the breastfed infant should be monitored for appetite changes, hormonal side effects, and proper weight gain/growth.[48201] One study found that low-dose CHCs (e.g., 10 mcg per day ethinyl estradiol) may not adversely affect lactation.[48200] However, a systematic review concluded that the available evidence, even from randomized controlled trials, is limited and of low quality; proper trials are needed.[48202] The World Health Organization (WHO) Contraceptive Criteria has recommendations that are more restrictive than USMEC; the WHO criteria state CHCs should not be used in breast-feeding individuals before 42 days after birth and that the disadvantages of CHC use generally outweigh the advantages between 6 weeks and 6 months after birth for individuals who are breast-feeding.[48204] Alternate contraceptive agents to consider for the breast-feeding individual include non-hormonal contraceptive methods (e.g., copper IUD, barrier methods, spermicides) and progestin-only contraceptives (e.g., medroxyprogesterone contraceptive injections, norgestrel oral contraceptive, levonorgestrel IUDs).[48201] HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY (HRT): Use estrogen-based HRT products with caution during breast-feeding. Estrogen administration has been shown to decrease the quantity and quality of the breast milk and detectable amounts of drug have been identified in the milk. A reduction in lactation can occur at any time but is less likely to occur once breast-feeding is well-established.[43360]
Cookies are used by this site. To decline or learn more, visit our cookie notice.
Copyright © 2025 Elsevier, its licensors, and contributors. All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.