Intrauterine Device (IUD): What to Know
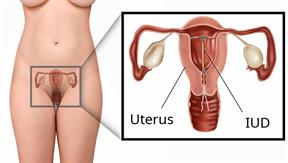
An intrauterine device (IUD) is put into your uterus to prevent pregnancy. It's a small, T-shaped device that has one or two nylon strings hanging down from it. The strings hang out of your cervix, which is the lowest part of your uterus. There are two types of IUDs.
- Hormone IUDs. Hormones are chemicals that affect how the body works.
- Copper IUDs.
How is an IUD put in?
An IUD is put in through your vagina, through your cervix, and into your uterus by your health care provider.
How is an IUD taken out?
Your provider will pull on the IUD strings to take the IUD out of your uterus.
How does an IUD work?
Progestin in a hormone IUD prevents pregnancy because it:
Copper in a copper IUD prevents pregnancy by making your uterus and fallopian tubes produce a fluid. This fluid kills sperm.
What are the advantages of an IUD?
Advantages of either type of IUD
An IUD:
Works really well to prevent pregnancy.
Can be taken out. You can become pregnant shortly after the IUD is taken out.
Is low maintenance.
Can stay in place for a long time.
Has no side effects from estrogen.
Can be used when breastfeeding.
Doesn't cause weight gain.
Can be put in right after childbirth, an abortion, or a miscarriage.
Advantages of a hormone IUD
If it's put in within 7 days of your period starting, it can prevent pregnancy right away. If the hormone IUD is put in at any other time in your cycle, you will need to use a backup method of birth control for 7 days after it's put in.
It can make periods lighter or stop.
It can reduce cramping from periods.
It can be used for 3–8 years. This depends on which IUD you have.
Advantages of a copper IUD
It works right after it's put in.
It can be used as a form of emergency birth control. It needs to be put in within 5 days after having unprotected sex.
It doesn't have any hormones in it.
It doesn't affect your body's natural hormones.
It can be used for up to 10 years.
What are the disadvantages of an IUD?
-
An IUD may cause spotting or bleeding between periods.
-
It's common to have pain when the IUD is put in. You may also have cramping and bleeding from your vagina after it's put in.
-
A copper IUD can make your period flow heavier and more painful.
-
IUDs can't prevent STIs. You need to use a condom to prevent STIs.
-
An IUD may cut the uterus, called a uterine perforation, when it's put in. This is rare.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) may happen after the IUD is put in.
PID is an infection in the uterus and fallopian tubes.
The IUD doesn't cause the infection.
The infection is from a sexually transmitted infection (STI). If this happens, it is usually during the first 20 days after the IUD is put in. This is rare.
This information is not intended to replace advice given to you by your health care provider. Make sure you discuss any questions you have with your health care provider.
 An intrauterine device (IUD) is put into your uterus to prevent pregnancy. It's a small, T-shaped device that has one or two nylon strings hanging down from it. The strings hang out of your cervix, which is the lowest part of your uterus. There are two types of IUDs.
An intrauterine device (IUD) is put into your uterus to prevent pregnancy. It's a small, T-shaped device that has one or two nylon strings hanging down from it. The strings hang out of your cervix, which is the lowest part of your uterus. There are two types of IUDs.